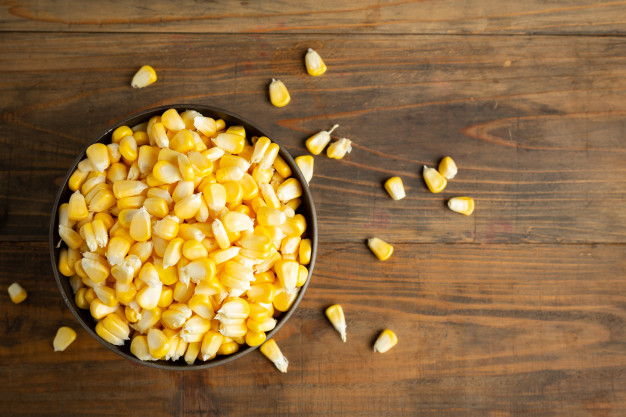
Biotin is a sulfur containing water soluble vitamin. It belongs to vitamin B complex family and it is known as vitamin B7 or Vitamin H. Another name of this vitamin is “anti-egg white injury factor”. It has shown that consumption of raw eggs is associated with the developing various neurological and skin problems and causes growth retardation. Later it had come to know that raw egg white contains an anti-vitamin named avidin that prevents biotin absorption. Deficiency of biotin was responsible for these complications. Consumption of cooked egg is not related with developing these complications as cooking destroys avidin and spares the biotin hence, biotin is known as “anti-egg white injury factor”.
Biotin is so important to utilize the carbohydrate, protein and fat completely by supporting their metabolism and enhancing energy production. It helps to regulate blood sugar level and helps in the growth of hair, eye, skin, liver and nervous system.
Sources
Foods rich in biotin are listed below –
- Meat (liver and kidney)
- Egg yolk
- Soybean and other soy products
- Cereal and grains
- Cauliflower
- Bananas
- Yeast
- Nuts
- Carrot
- Tomatoes
- Milk and dairy products
- Salmon fish

It is beneficial to consume biotin from natural sources but if it is not possible then it can be consumed through supplements.
Health benefits of biotin
Role on metabolism
- Biotin is one of the most important B vitamins and helps to regulate the metabolic process of carbohydrate, protein and fat. Proper metabolism of these three food constituents are related with providing sufficient energy to body as well as helps to prevent various metabolic disorders
- Biotin acts as co-factor for the enzyme carboxylase, which is an essential enzyme required for the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates
- Pyruvate carboxylase is a biotin depended enzyme that stimulates neoglucogenesis (synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate source) process. It has found that when glucose deficiency (hypoglycemia) occurred in body then neoglucogenesis helps to produce glucose and overcome its deficiency
- The enzyme Acetyle CoA carboxylase utilized biotin for its activity and is responsible for the biosynthesis of fatty acids, apart from that it also helps in the synthesis of various amino acids
Role on the growth and development of cells and tissues
- Biotin helps in synthesis of cells and their proper growth by stimulating cell division
- It has found that biotin plays an indispensable role on re-synthesizing tissues and repairing tissue damage
- It helps to rebuild muscle tissues and promotes their function

Role on thyroid hormones
- Biotin plays an important role in maintaining the activities of thyroid gland and makes it properly functioning resulting in proper secretion of thyroxin hormone within the body
- Biotin is utilized to regulate the activities of thyroid gland
- It also helps to prevent hyper and hypothyroidism
Role on pregnancy and fetus development
- Biotin should be consumed during pregnancy as it promotes intrauterine growth and it also helps in the development of the fetus
- It has found that those pregnant women who consume biotin during their gestational periods, will give birth healthy infants and experienced less pregnancy complications
Role on the growth and development of hair, nail and skin
- Keratin is an important protein which is required for the formation of hair, skin and nails.
- Biotin helps in the synthesis of keratin leading to the growth of hair, nails and skin
- It has found that biotin is responsible for increasing the thickness of hair
- Biotin helps in strengthening nails and helps to promote respective growth. It has shown that those individuals who consume biotin sufficiently have comparatively 20 to 25% strengthen nails and incidence of splitting or breakage of nail is lesser
- Biotin plays significant roles in the growth of skin as it provides adequate nourishment to the skin hence improves skin health and it helps to increase the skin glow
- It also helps to prevent skin diseases like itchy skin, blisters, rashes, dry skin and several dermatological disorders

Role on nervous system
- Biotin influences the activity of neurotransmitter hence helps in the transduction of nervous stimuli throughout the body
- It is is required to enhance the function of central and peripheral nervous system
- It is associated with increasing memory and concentration.
- It has also found that it helps to prevent Alzheimer’s disease, dementia and various neurodegenerative disorders
Recommended dietary allowance of Biotin
Biotin should be consumed through diet or supplements to achieve a healthier nutritional status. The recommended dietary allowance of biotin is about 100 to 300mg per day for adults. An individual can get sufficient biotin if he or she consumes a healthy diet but recently it has seen that many people consume biotin through supplementary products. Tough it is beneficial to consume biotin from natural sources as consuming too much dietary biotin does not cause toxicity.
Deficiency disorders and toxic symptoms of biotin
It has estimated that if biotin is not consumed according to the recommendation then it would cause various health hazards, if it is consumed in lesser amount or in higher amount than normal recommendation then it causes several deficiency disorders or toxic symptoms.

The following table shows both effects of biotin consumption –
| Deficiency disorders of Biotin | Toxic symptoms of Biotin |
| Biotin deficiencies can lead to –
|
|
Recent researches on biotin
Various researches have been carried out on biotin in recent years, which have shown some unique biochemical function of biotin associated with improving the health in many folds. The outcome of the researches is discussed below –

Role of biotin supplements on diabetes
- Researchers have shown that biotin has a stimulatory action on the β cell of pancreas and helps to increases the insulin secretion from pancreas (Yan and Khalil, 2017)
- It helps to reduce the glycemic load of blood by transporting glucose from blood vessels to liver where it facilitates glucose storage
- It helps to prevent both type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- Consumption of biotin supplements (doses recommended by physician) are used as a preventive measure of diabetes
Role of biotin on weight loss
Recent studies have shown that biotin is related with increasing the metabolic rate of an individual and helps to regulate the energy balance. Consumption of biotin along with chromium can increase the catabolic processes of the body and leads to weight reduction (Järvinen et al., 2016)

Source:
Järvinen, E., Ismail, K., Muniandy, M., Bogl, L.H., Heinonen, S., Tummers, M., Miettinen, S., Kaprio, J., Rissanen, A., Ollikainen, M. and Pietiläinen, K.H., 2016. Biotin-dependent functions in adiposity: a study of monozygotic twin pairs. International Journal of Obesity, 40(5), pp.788-795.
Li, D., Radulescu, A., Shrestha, R.T., Root, M., Karger, A.B., Killeen, A.A., Hodges, J.S., Fan, S.L., Ferguson, A., Garg, U. and Sokoll, L.J., 2017. Association of biotin ingestion with performance of hormone and nonhormone assays in healthy adults. Jama, 318(12), pp.1150-1160.
Lipner, S.R., 2018. Rethinking biotin therapy for hair, nail, and skin disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, 78(6), pp.1236-1238.
Liu, W., Samanta, S.K., Smith, B.D. and Isaacs, L., 2017. Synthetic mimics of biotin/(strept) avidin. Chemical Society Reviews, 46(9), pp.2391-2403.
McCarty, M.F. and DiNicolantonio, J.J., 2017. Neuroprotective potential of high-dose biotin. Medical hypotheses, 109, pp.145-149.
Mock, D.M., 2017. Biotin: from nutrition to therapeutics. The Journal of nutrition, 147(8), pp.1487-1492.
Patel, D.P., Swink, S.M. and Castelo-Soccio, L., 2017. A review of the use of biotin for hair loss. Skin appendage disorders, 3(3), pp.166-169.
Trüeb, R.M., 2016. Serum biotin levels in women complaining of hair loss. International journal of trichology, 8(2), p.73.
Yan, M.K.W. and Khalil, H., 2017. Vitamin supplements in type 2 diabetes mellitus management: a review. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 11, pp.S589-S595.




