Creatine is a biochemical substance produced from amino acids within body. It has seen that after consumption, protein gets digested, absorbed and metabolized within body. During its metabolism, creatine is produced primarily in liver and to some extent in pancreas and kidney. It is associated with storing the high energy phosphate group within body in the form of phosphocreatine. When required it donates its phosphate group to adenosine-di-phosphate or ADP to from adenosine-triphosphate or ATP (ADP + Pi = ATP). It is generally used for enhancing energy level within body and related with enhancing muscle growth, mass and strength that helps to improve the endurance and body’s ability to cope up with general stress.
Mechanism of action
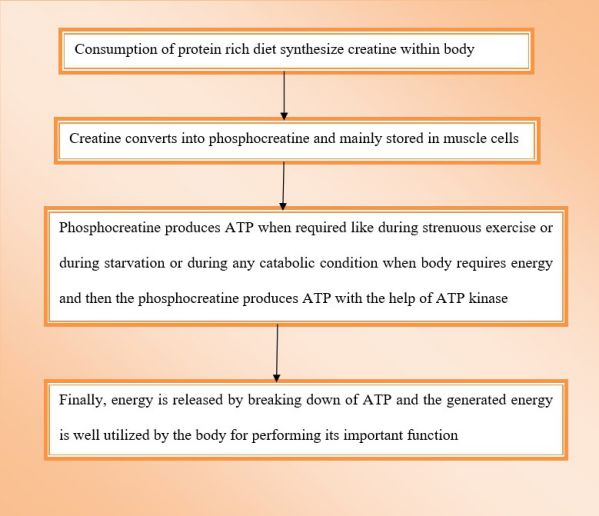
Below chart will depict the mechanism of creatine’s action within the body –
Health benefits
Role on muscle growth
- Creatine is one of the most effective substances required for muscle growth. It helps to enhance the secretion of growth hormones and other anabolic hormones such as insulin-like growth factor that stimulates the muscle growth
- It enhances protein synthesis that leads to the formation of new muscle fibre
- It helps to increase water content within muscle that is related with enhancing muscle volume
- Creatine is responsible for improving the process of cell signaling that promotes neuromuscular functionality and leads to new muscle cells growth
- Myostatin is a protein that is responsible for inhibiting muscular growth. Creatine helps to reduce the level of myostatin and supports muscle growth
- It also helps in increasing muscle mass

Role on energy production
- Creatine stored in muscle in the form of phosphocreatine and later produce high energy compound ATP, which is later utilized by cells of the body
- During exercise, the muscle produces ATP from phosphocreatine and breaks ATP for releasing energy that helps to enhance the ability of the body to continue its function
Role on performance
- Creatine helps to improve endurance by preventing muscle fatigue and weakness during exercise
- It is associated with enhancing muscle mass, strength, ballistic power, functionality and sprint power that is associated with supporting the high intensity performance

Role on brain function
- Creatine has significant role in maintaining proper brain functioning
- Brain cell also stores phosphocreatine and through which it utilizes ATP for its optimum performance
- It also helps to improve the memory

Role on cardiovascular system
- It helps to reduce the elevated concentration of triglycerides within body and helps to maintain the lipid profile in normal range
- It helps to reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis and inflammation of heart which is associated with protecting the cardiac system
Role on preventing neurological disorders
- Creatine helps to increase phosphocreatine storage in brain cells and helps to regulate the release of neurotransmitter which is allied with reducing the risk of developing neurological disorders
- Creatine can be used as an effective remedial action for various neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, motor neuron disorders and malfunctioning of brain
Role on preventing diabetes
- It has seen that consumption of creatine or its supplements is related with decreasing blood sugar level
- Creatine helps to increase the function of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT-4) which is responsible for binding with glucose molecule and transport it from blood vessels to muscle leads to reducing the concentration of free sugar in blood
Others health benefits
- It helps to prevent general weakness and fatigue by enhancing the energy level within body
- It also helps to prevent dizziness
- It is associated with maintaining acid base balance and energy balance of body hence, related with maintaining homeostasis
- It also helps to prevent oxidative stress of body

Effect of consuming creatine
Consumption of creatine is very healthy, and it provides both short term and long-term effects within body. The short-term effects of creatine include weight gain mainly due to increase in muscle mass and due to retention of water within muscle leading to enhancing the water weight in the body. It has also seen that consumption of creatine is associated with enhancing about two to four pounds of body weight. Whereas the long-term effects of creatine are related with promoting the muscle metabolism results in enhancing the strength of muscle that makes the body accustomed with strenuous workload
Creatine therapy
It is a type of therapy that helps to improve various pathological conditions with the help of creatine administration which includes –
Creatine administration for improving the health of dialysis patient
- It helps to improve the overall health status and the survival rate of dialysis patient and patients suffer from chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Excessive depletion of creatine occurred from the skeletal and cardiac muscle in patients with dialysis and CKD that leads to cellular damage and deterioration in neurological and musculo skeletal system. Thus, administration of creatine would help to counteract the depletion and prevents the damages
- It has seen that consumption of creatine is associated with enhancing the energy production among the patients which is associated with improving the symptoms

Creatine for improving reproductive cycle
- Several researches have shown that creatine, phosphocreatine and creatine kinase expression helps in the production of high energy compound (ATP) and also associated with regulating the energy metabolism and energy turnover. Disruption in this energy circuit adversely affect the reproductive cycle of females (Ellery et al., 2016)
- Creatine supplementation is beneficial for female as it helps to support the increased requirement of calorie during pregnancy and lactation
- The bioavailability of creatine helps to optimize the health outcomes
Creatine for preventing myogenic oxidative stress
- Various researches have shown that creatine administration is associated with preventing the differentiation arrests due to the oxidative stress of myoblast and hence helps to enhance the functionality of entire muscular system of body (Barbieri et al., 2016)
- It has seen that creatine supplement acts as an effective therapeutic agent for the prevention of myopathy and muscle wasting
General considerations of consuming creatine
- It is safe to consume creatine or its supplements orally
- It is naturally present in meat hence vegans are more prone to develop its deficiency and leads to develop muscle wasting, malnutrition and general weakness
- Consumption of creatine from natural sources does not cause any side effects but prolong consumption of creatine supplements may develop several complications like anxiety, gastrointestinal disorders, fever, headache, skin rashes, nausea and vomiting
- It is better especially for children to avoid creatine supplementation
- Individual who suffer from liver disorders or renal problems should consult with physician or nutritionist before consuming creatine supplements


Source:
Albl, A.A., 2018. A Review of Creatine and Its Role in Muscle Strength and Balance. Heart, 22, p.24.
Barbieri, E., Guescini, M., Calcabrini, C., Vallorani, L., Diaz, A.R., Fimognari, C., Canonico, B., Luchetti, F., Papa, S., Battistelli, M. and Falcieri, E., 2016. Creatine prevents the structural and functional damage to mitochondria in myogenic, oxidatively stressed C2C12 cells and restores their differentiation capacity. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2016.
Butts, J., Jacobs, B. and Silvis, M., 2018. Creatine use in sports. Sports health, 10(1), pp.31-34.
Dolan, E., Gualano, B. and Rawson, E.S., 2019. Beyond muscle: the effects of creatine supplementation on brain creatine, cognitive processing, and traumatic brain injury. European Journal of Sport Science, 19(1), pp.1-14.
Ellery, S.J., Walker, D.W. and Dickinson, H., 2016. Creatine for women: a review of the relationship between creatine and the reproductive cycle and female-specific benefits of creatine therapy. Amino Acids, 48(8), pp.1807-1817.
Kreider, R.B., Kalman, D.S., Antonio, J., Ziegenfuss, T.N., Wildman, R., Collins, R., Candow, D.G., Kleiner, S.M., Almada, A.L. and Lopez, H.L., 2017. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), pp.1-18.
Wallimann, T. and Harris, R., 2016. Creatine: a miserable life without it.
Wallimann, T., Riek, U. and Möddel, M., 2017. Intradialytic creatine supplementation: A scientific rationale for improving the health and quality of life of dialysis patients. Medical Hypotheses, 99, pp.1-14.


