Dark chocolate is a very popular form of chocolate, made up of cocoa butter, cocoa solid and sugar. Dark chocolate contains comparatively lesser sugar than other chocolates and its nutritive value entirely depends on its cocoa content. It has seen that chocolate which contains excessive cocoa (dark chocolate) is bitterer in taste and does not contain much sugar. Hence consumption of such chocolate is considered as healthy.
Characteristics
- It is bitter in taste
- Presence of cocoa in dark chocolate is responsible for its bitter taste. It has seen that increase in cocoa content increases the bitterness of dark chocolate
- It is basically a suspension (solid) of cocoa powder and sugar in cocoa butter and it has no added milk solid
- It is dark brown in color
Nutritional profile
- As mentioned above, nutritional value of dark chocolate is entirely depending upon its cocoa content. General healthy dark chocolate contains 70 to 85% of cocoa
- It also contains significant amount of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. It produces adequate calories during its oxidation due to its macronutrients components
- It contains significant amount of fibre as well
- It contains several vitamins like Vitamin A, Vitamin K, thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine and cyanocobalamin
- It also contains various trace elements such as zinc, copper, iron, potassium, magnesium, selenium and manganese
- It contains several bioactive compounds also that exert strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, which include caffeine, theobromine, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, resveratrol, phenylethylamine, glucoside, quercetin, flavan-3-ols, epicatechin and catechin

Dark chocolate is healthier than milk chocolate
Dark chocolate contains comparatively high amount of cocoa solid than milk chocolate and has no added milk solid. It also contains relatively lesser amount of sugar hence it is beneficial to consume dark chocolate than milk chocolate as it produces fewer calories. It has also seen that dark chocolate is richer in fibre content than milk chocolate. So, consumption of dark chocolate is healthier and it can also be considered as a better option for obese individuals as well as for diabetic patients.
Processing
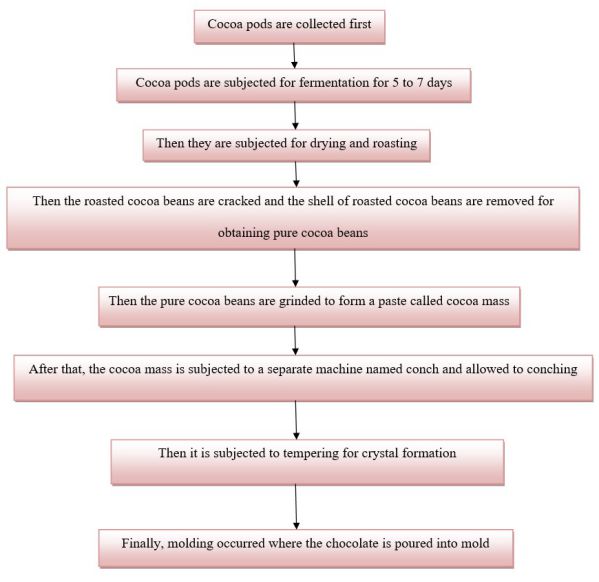
Below chart will depict the processing of dark chocolate
Health benefits
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory property
- Polyphenols and flavanols components of dark chocolate exert strong antioxidant property and help to protect the body from oxidative damages
- It helps to protect vital cellular components like DNA, RNA, proteins and lipids from oxidation
- It helps to reduce the concentration of free radicals by effectively scavenging them
- The antioxidant activities of dark chocolate are associated with reducing the prevalence of cancers as well
- It also exerts anti-inflammatory effects and help to reduce the prevalence of inflammatory events within body hence reduces the risk of developing degenerative diseases

Role on cardiovascular system
- Cocoa content of dark chocolate has cardio protective effects. It helps to reduce inflammatory events of heart such as, ischemic heart diseases, thrombosis, and myocardial infraction
- Flavonoid components of dark chocolate help to reduce the concentration of LDL and also helps to prevent LDL oxidation hence reduces the risk of atherosclerosis
- It is also associated with improving HDL level within body
- It helps to prevent hypertension as it enhances blood circulation
- It also helps in vasodilatation
- It helps to reduces the prevalence of strokes
Role on preventing diabetes
- Though consumption of chocolate daily is not good for diabetic patient (as it contains both sugar and fat) but it has seen that consuming low sugar dark chocolate at least once a week helps to reduce elevated blood sugar level
- The flavonoids contents of dark chocolate help to increase the sensitivity of insulin as it helps to reduce insulin resistance by inhibiting oxidative stress

Role on nervous system
- Consumption of dark chocolate is related with increasing blood flow to brain that helps to deliver sufficient oxygen and nutrients to brain cells that promotes their functionality and prevents oxidative damages of brain and ageing
- Theobromine and caffeine component of cocoa can also be able to improve brain function in a short duration
- It helps to improve general alertness and task performing abilities
- It has seen that consumption of cocoa with high flavanol contents improve memory and cognitive ability
Role on mental health
- Flavanols of dark chocolate is responsible for improving mood and helps to refresh the mind
- It also helps to reduce depression
Role on skin
- Flavonols components of dark chocolate are responsible for increasing blood flow to skin, which is associated with enhancing skin hydration and density
- It helps to protect the skin from sun damage
Role on gastrointestinal health
- Dark chocolate acts as an effective prebiotic
- The antioxidant and fibre component of dark chocolate are fermented by intestinal beneficial microbes, which help to enhance their growth and population that are associated with improving bowel health, nutrient absorption and metabolism
Clinical significance
- Recent researches have shown that the cocoa and polyphenol components of dark chocolate are responsible for triggering some signaling pathway like signal transducer or toll-like receptor 4 or nuclear factor κB and transcription activator, which help to induce immunological responses, genetic expression and cellular metabolism (Magrone et al., 2017)
- It helps to release nitric oxide by activating endothelial NO synthase (an enzyme), which is responsible for exerting cardio protective effects and also facilitates vasodilatation and thus prevents hypertension
- It also helps to improve the symptoms of metabolic syndrome, neurological and gastrointestinal disorders in human
Recent findings
- Simple fatty liver steatosis can lead to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis if endothelial dysfunction occurred within body. Oxidative stress is the principal causative factor of endothelial dysfunction. Recent researches have shown that consumption of dark chocolate helps to prevent non-alcoholic steatohepatitis as it helps to reduce oxidative stress. It also helps to restore endothelial function by inhibiting the activity of nicotinamide-adenine-dinucleotide-phosphate oxidase 2 (Loffredo et al., 2018)
- Current studies have shown that consumption of dark chocolate containing 70% cocoa helps to improve gamma wave (the fastest brain wave responsible for cognitive ability) in brain during visualization of exercise and rest (Silver et al., 2018)
Risk factors
- Dark chocolate provides sufficient calories as it contains significant amount of fats and sugars. Hence excessive consumption of dark chocolate should be avoided otherwise it can lead to obesity and may also develop diabetes and cardiovascular disease in later
- We know that dark chocolate contains significant amount of caffeine. So, its excessive consumption may develop caffeine related complications like insomnia, nervousness and it also increases heartbeat
- Regular consumption of dark chocolate may also cause gastrointestinal disturbances like nausea, vomiting, flatulence
- Individuals suffer from irritable bowel syndrome should avoid its consumption


Source:
Chudzińska, M., Pietrzak, J., Węglarz, M., Wołowiec, Ł., Rogowicz, D., Zukow, W. and Sinkiewicz, W., 2017. Chocolate protects a heart and vessels. Journal of Education, Health and Sport, 7(8), pp.510-524.
Loffredo, L., Baratta, F., Ludovica, P., Battaglia, S., Carnevale, R., Nocella, C., Novo, M., Pannitteri, G., Ceci, F., Angelico, F. and Violi, F., 2018. Effects of dark chocolate on endothelial function in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, 28(2), pp.143-149.
Magrone, T., Russo, M.A. and Jirillo, E., 2017. Cocoa and dark chocolate polyphenols: from biology to clinical applications. Frontiers in Immunology, 8, p.677.
Patel, N., Jayswal, S. and Maitreya, B.B., 2019. Dark chocolate: Consumption for human health. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 8(3), pp.2887-2890.
Patturaja, K., Gayathri, R. and Vishnupriya, V., 2016. Effect of Dark Chocolate in Regulating Blood Pressure-Systematic Review. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 9(9), pp.1505-1507.
Silver, S., Al-Tikriti, R. and Jin, N., 2018. Dark Chocolate (70% Cacao) Modulates Gamma Wave Frequencies in Vigorously Active Individuals.
Yuan, S., Li, X., Jin, Y. and Lu, J., 2017. Chocolate consumption and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrients, 9(7), p.688.
Zugravu, C. and Otelea, M.R., 2019. Dark chocolate: To eat or not to eat? A review. Journal of AOAC International, 102(5), pp.1388-1396.




