Glucosamine is a monosaccharide (the simplest form of sugar) present abundantly in body when protein (amino acids) binds with sugar (glucose) then it forms glucosamine. It is also termed as amino sugar. It is mainly derived from chitosans, polysaccharides and chitins and acts as a precursor for the synthesis of glycosylated protein (glucose + protein). The main glycosylated proteins synthesized by glucosamine are glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans. These act as potential building blocks of body which helps in the synthesis and growth of cartilage, tendon, ligaments and synovial fluid. It is primarily used for treating bones and joints disorders and used as a preventive measure for arthritis. It also helps to prevent inflammations and hence helps to reduce the feeling of pain. Recently glucosamine is supplemented with various scientific methods and is used by a wide range of people. Basically, it is found in three forms which are glucosamine sulphate, glucosamine hydrochloride and N-acetyl glucosamine among which, most healthy amino sugar is glucosamine sulphate.
Glucosamine sulphate is responsible for the production of fluids that surround the joints, cartilage, bone and tendons and also helps to protect them from external injuries. On the other hand, glucosamine hydrochloride is related to build up a cushion like structure that surrounds the joint and helps to prevent joint to joint collision. Whereas, N-acetyl glucosamine shows its effect on treating arthritis, ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, crohn’s diseases, knee pain and aging of skin.

Source
- Glucosamine is abundantly present in body and generally found in bone, bone marrow and around the joints
- It is also present in shell fishes like lobster, shrimp
- It can be also obtained by consuming supplements which are generally synthesized in laboratories using efficient scientific method. For example, glucosamine sulphate is prepared from the shells of shellfish and commonly used as an effective dietary supplement for preventing various abnormalities of joints
- As mentioned above there are mainly three forms of glucosamine commercially available as dietary supplements and are extensively used
- All of these are the basic sources of glucosamine but before consuming glucosamine, it should be kept in mind that, if an individual have allergies in shell fish then it should be consumed carefully with proper dietary consideration recommended by nutritionist for avoiding health risks. Whereas it can also consumed through supplements but individual who suffer from diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, bleeding disorders and renal disorders should consult physician before taking glucosamine supplements
Health benefits of glucosamine
Role on preventing arthritis
- Inflammation of joints is referred to as arthritis. It has found that when the joints are inflamed, they tend to develop stiffness, swelling, pain, warmth and redness. Glucosamine helps to improve these symptoms of arthritis (especially osteoarthritis)
- Glucosamine helps to synthesize aggrecan, an important substance of cartilage. Aggrecan helps to enhance the hydrophilicity of cartilage which is associated with maintaining its structure and protect the cartilage inside the joints from damages and helps to inhibit joint inflammation

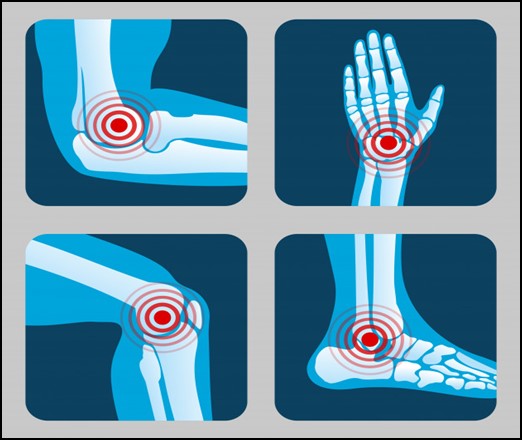
- It has shown that in arthritis the cartilage become thin due to its breakdown which causes stiffness of joints with frequent frictions and severe pain. Glucosamine helps to protect the cartilage from becoming thin by preventing its breakdown and increases the synthesis of fluids that surround the joints. This is the most important feature responsible for delaying the structural progression of arthritis
- It also helps to prevent the narrowing of joint space and reducing the incidence of friction thus reduces pain
- It is mainly beneficial for knee and hip arthritis and it is recommended to consume about 1500mg of glucosamine (glucosamine sulphate) daily to prevent arthritis. It has also found that if the consumption of glucosamine is not continued, still it provides its beneficial action up to next three months
Role on inflammation
- It has found that glucosamine has anti-inflammatory property and helps to prevent inflammation and pain
- It helps to reduce the level of pro-inflammatory factors like interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and increases proteoglycans synthesis, which is associated with decreasing the breakage of cartilage
- Promoting cartilage health is related with improving joint functions
Role on joints and its effect on treating bone and joint disorders
- Glucosamine has joint protective effect and it is associated with synthesizing new tissues between joints
- A smooth white tissue named articular cartilage is one of the most vital tissues produced by glucosamine present at the end of bones and helps to it. They are met there (end of each bone) to initiate joint formation
- It is found that these tissues along with synovial fluid (a lubricating substance) help the bone to move flexibly without any friction and helps in the painless movements of joints

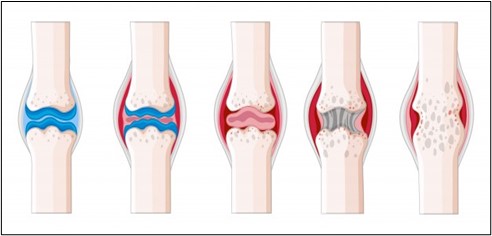
- It also helps to prevent various joint disorders by inhibiting the breakdown of cartilage and it also helps to enhance cartilage repairing mechanism
- Glucosamine supplements are largely used to treat adverse joint and bone conditions by delaying disease progression, maintaining proper joint space and reducing pain
Role on preventing other diseases
- Glucosamine helps to prevent several degenerative diseases (shorter and long term) and associated with reducing their symptoms and severity
- It has found that those individual who have low glucosamine concentration in their body are prone to develop several degenerative diseases like – Ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, interstitial cystitis, all of this are very common gastrointestinal disorders and are responsible for damaging entire functions of gastrointestinal tract and related organs. Glucosamine helps to prevent this condition and promotes better gastrointestinal health
- It also helps to prevent glaucoma, multiple sclerosis, joint pain, back pain, osteoarthritis and obesity

Role on heart
- It has found that individual who consume glucosamine have lower risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Generally, glucosamine helps to reduce the prevalence of strokes
- Mainly glucosamine hydrochloride and N-acetyl glucosamine are better utilized for cardiac health
Side effects of consuming excessive glucosamine
- As mentioned above glucosamine is widely used for its potential health benefits but consuming too much can causes several health hazards
- It has shown that it increases the blood sugar level among diabetic patient and deteriorate the situation, hence people suffer from diabetes should consult physician before consuming it
- It may increase pressure within eye and affects the vision adversely and worsen glaucoma
- It also causes some gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, heart burn, diarrhea, constipation and abdominal pain
- It often causes allergic reaction in people (who have shellfish allergy) and associated with developing rashes, blisters, redness and itching of skin
So, it can be stated that glucosamine is one of the most imperative constituents required for healthy cartilage and joints. Recently, arthritis becomes a very common health complication especially among older person (where females are more prone than males) because the strength of cartilage started to decrease with age and get collapsed which causes swelling and friction of joints while movements lead to developing arthritis. Glucosamine is widely used as one of the most effective measures for treating osteoarthritis and related joint disorders. Consumption of glucosamine along with Vitamin D is healthier to improve the symptoms of arthritis. It should be consumed in required amount for treating joint disorders as well as to avoid its harmful side effects.

Source:
Al-Saadi, H.M., Pang, K.L., Ima-Nirwana, S. and Chin, K.Y., 2019. Multifaceted Protective Role of Glucosamine against Osteoarthritis: Review of Its Molecular Mechanisms. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 87(4), p.34.
Dalirfardouei, R., Karimi, G. and Jamialahmadi, K., 2016. Molecular mechanisms and biomedical applications of glucosamine as a potential multifunctional therapeutic agent. Life sciences, 152, pp.21-29.
Esfandiari, H. and Loewen, N.A., 2019. Effect of glucosamine on intraocular pressure. In Handbook of Nutrition, Diet, and the Eye (pp. 333-338). Academic Press.
Hume, A.L., 2019. Glucosamine and chondroitin. Pharmacy Today, 25(7), p.16.
Jamialahmadi, K., 2019. Beneficial applications of glucosamine. In Molecular Nutrition: Carbohydrates (pp. 319-336). Academic Press.
Kucharz, E.J., 2019. Hit two birds with one stone: why crystalline glucosamine sulphate used for osteoarthritis medication is beneficial for patients with risk of cardiovascular disorders. Reumatologia/Rheumatology, 57(5), pp.306-306.
Ma, Q. and Gao, X., 2019. Categories and biomanufacturing methods of glucosamine. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 103(19), pp.7883-7889.
Sanders, M., Morrissey, H. and Ball, P., 2018. Consumers' perception of the efficacy and tolerance of glucosamine in joint diseases.



