Glycine is an amino acid, which helps in the biosynthesis of proteins within body. Glycine is a non-essential and simple form of amino acid that can be synthesized by body hence if it is not taken from diet it would not cause such deficiency. Natural protein rich foods contain glycine in significant amount, so consumption of such food can easily meet the requirement of glycine. Though it is synthesized by body, but it should be consumed through daily diet for maintaining the internal balance of glycine. The main function of glycine is to treat schizophrenia and related neurological disorders.
The potential health benefits of glycine make it more worthy and now it is commercially available as supplementary product and widely used to fight against malnutrition.
Chemistry
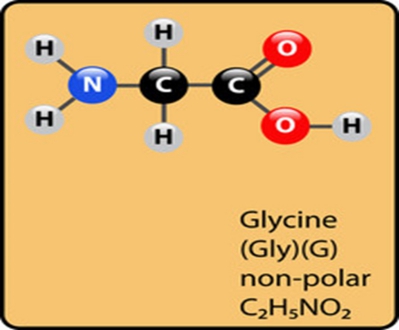
- Glycine is a monoamino and monocarboxylic acid, acts as building block of protein. It has found that several glycine molecules are bound with each other through peptide bonds and help to form protein
- It contains aliphatic side chain in its structure
- The formula of glycine is CH2-NH2-COOH
- It is consisting of one amino group, one carboxylic group, two hydrogen and one carbon atom
- It is colorless, sweet in taste and crystalline solid in nature
- It is a proteinogenic amino acid. The amino acid which is incorporated into protein during protein synthesis is known as proteinogenic amino acid


Sources
Human can synthesize glycine within body and furthermore it can be obtained through diet (natural source) or by taking supplements. Consumption of glycine from natural source is comparatively healthy than taking supplements as consumption of excessive dietary glycine does not cause any toxicity but consuming too much supplement can cause various health hazards.
The below table gives a good overview of the various sources of glycine
| Amino acids that synthesize glycine in body | Food stuffs that contain glycine |
|
|
Needs of glycine in daily life
Apart from treating schizophrenia, glycine is required to treat several other diseases which include –
- Diabetes
- Kidney failure
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Psychotic Disorders among Children
- Ulcers on legs
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Heart attacks
- Metabolic disorders (inherited)
- Glycine helps to protect kidney from the injurious side effects of drugs mainly used after kidney transplantation

Risks of glycine metabolic disorder
Disorders of glycine metabolism are very harmful and associated with developing several diseases. It should treat properly otherwise it would become fatal. The harmful effects of this impaired metabolic syndrome include –
Glycine encephalopathy
- Several researches and studies have shown that impaired glycine metabolism is responsible for the development of glycine encephalopathy (Alfadhel et al., 2016). Glycine encephalopathy is an inherited metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by deficiency of glycine splitting enzyme, mainly caused by gene mutation
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes dramatic increase in the concentration of glycine that interferes with normal glycine functions
- Glycine acts as chemical messenger and helps in the transmission of signal or stimuli in brain but abnormalities in glycine level hamper this function and causes various neurological disorders like intellectual disabilities, behavioral problems, optical atrophy (vision loss caused by damages of nerves present in eyes), lethargy and hypotonia (poor muscle tone)
Argininie Glycine amidinotransferase Deficiency
- Argininie glycine amidinotransferase is an enzyme, which is required in Creatine metabolism and deficiency of this enzyme results in irregular formation and transportation of creatine
- Improper utilization of glycine can cause the argininie glycine amidinotransferase deficiency
- This condition is known as cerebral creatine deficiency syndrome and characterized by delayed speech, seizure activity and intellectual disabilities

Health benefits of glycine
Here we will discuss the health benefits of glycine
Role on preventing schizophrenia
- Schizophrenia is a mental disorder which affects the ability of an individual to think and behave clearly. It also affects the emotional exposure, memory, capacity of concentration and cognitive abilities
- Blockage in N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors is responsible for developing schizophrenia. Several studies and researches have shown that glycine helps to inhibit this blockage and enhances the release of NMDA receptor mediated neurotransmitter, which helps to prevent the severity of schizophrenia and improves the health condition (de Bartolomeis et al., 2020)
Role on nervous system
- It has found that glycine plays several important roles on the growth and functioning of central and peripheral nervous system
- A range of studies and researches have shown that Glutamate is a neurotransmitter, which is associated with the normal functioning of central nervous system and deficiency of glutamate is responsible for developing various neuropsychiatric disorders like Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer disease and Dementia (Cleveland, 2016).
- All of these disorders can be prevented by administration of glycine in daily diet as glycine acts as a co agonist and helps to increase the releasing of neurotransmitter, which can improve the symptoms of neuropsychiatric disorders

Role on Diabetes
- Different researches and studies have shown that glycine helps to improve insulin resistance, which enhances glucose uptake from blood vessels and transport it into liver for storage, resulting in the reduction of glucose in blood stream (Yan-Do and MacDonald, 2017)
- It has also found that glycine enhances impaired insulin response among those people who are not diabetic
- It is widely used as a preventive measure for type 2 diabetes mellitus
Role on heart
- Glycine helps the body to utilize nitric oxide completely. Nitric oxide is related with increasing blood flow and hence able to reduce blood pressure
- Proper blood circulation helps to prevent artherosclerosis, stiffness and narrowing of blood vessels therefore reduces the risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease
Role on sleep
- Glycine helps to increase the secretion of serotonin, which helps to reduce insomnia and promotes the quality of sleep and it also helps to complete every phase of sleep cycle
- Glycine helps to reduce the core body temperature and so contributing a calming effect on brain and facilitates healthy sleeping
- Proper sleeping is associated with refreshment hence it can be stated that glycine has a relation with refreshment and enhances the body’s ability to perform well
 Other health benefits of glycine
Other health benefits of glycine
- Glycine helps in collagen formation. Collagen is one of the most important structural proteins of human body and it is consisting of glycine. It has seen that collagen contain glycine at third to fourth position of its structure
- Muscle wasting is a hazardous complication that causes reduction in muscle strength and mass leading to poor muscle functions. This complication can be prevented with daily consumption of glycine as it helps to prevent muscle loss
So, it can be stated that daily consumption of glycine is good for health, but it is better to avoid glycine if clozapine (antipsychotic medicine) is taken daily. As mentioned above excessive consumption of dietary glycine is not harmful but it is beneficial to consume glycine supplements less than 8g per day otherwise it would cause several gastrointestinal difficulties like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, indigestion and irritation in stomach.
Source:
Adeva-Andany, M., Souto-Adeva, G., Ameneiros-Rodriguez, E., Fernandez-Fernandez, C., Donapetry-Garcia, C. and Dominguez-Montero, A., 2018. Insulin resistance and glycine metabolism in humans. Amino Acids, 50(1), pp.11-27.
Alfadhel, M., Nashabat, M., Al Qahtani, H., Alfares, A., Al Mutairi, F., Al Shaalan, H., Douglas, G.V., Wierenga, K., Juusola, J., Alrifai, M.T. and Arold, S.T., 2016. Mutation in SLC6A9 encoding a glycine transporter causes a novel form of non-ketotic hyperglycinemia in humans. Human genetics, 135(11), pp.1263-1268.
Cleveland, W.L., 2016. High-dose glycine as a treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder and obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorders. U.S. Patent 9,504,665.
de Bartolomeis, A., Manchia, M., Marmo, F., Vellucci, L., Iasevoli, F. and Barone, A., 2020. Glycine Signaling in the Framework of Dopamine-Glutamate Interaction and Postsynaptic Density. Implications for Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11.
Koopman, R., Caldow, M.K., Ham, D.J. and Lynch, G.S., 2017. Glycine metabolism in skeletal muscle: implications for metabolic homeostasis. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care, 20(4), pp.237-242.
Li, P. and Wu, G., 2018. Roles of dietary glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline in collagen synthesis and animal growth. Amino acids, 50(1), pp.29-38.
Razak, M.A., Begum, P.S., Viswanath, B. and Rajagopal, S., 2017. Multifarious beneficial effect of nonessential amino acid, glycine: a review. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2017.
Yan-Do, R. and MacDonald, P.E., 2017. Impaired “glycine”-mia in type 2 diabetes and potential mechanisms contributing to glucose homeostasis. Endocrinology, 158(5), pp.1064-1073.
Yu, A. and Lau, A.Y., 2018. Glutamate and glycine binding to the NMDA receptor. Structure, 26(7), pp.1035-1043.