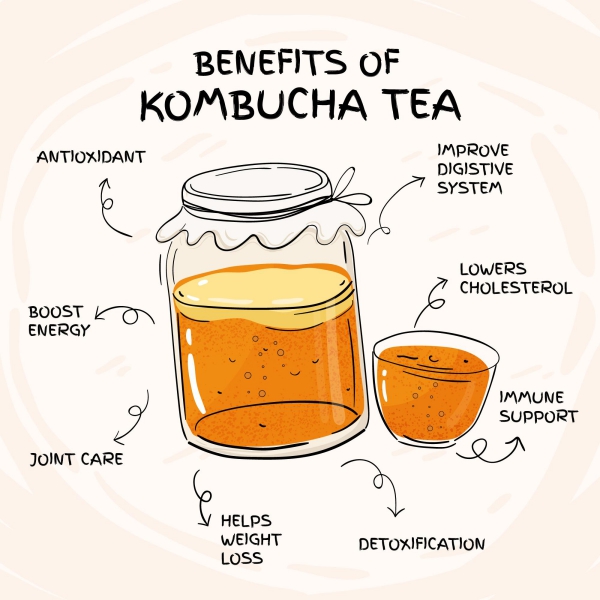
Kombucha is a healthy and fizzy beverage made up of yeast, bacteria, sugar and tea. It performs various important biological functions within body.
Nutritional composition
- It contains very less amount of carbohydrates
- It does not contain fat
- It does not produce enough calories on its oxidation hence it is known as low calorie beverage
- It contains various micronutrients like Vitamin C, Vitamin B1, B6, B12, sodium, zinc, copper, iron and manganese
- It also contains lactic acid, acetic acid and numerous beneficial bacteria
- It is packed with polyphenolic compounds, which play a number of biological roles within body
- It contains significant amount of antioxidant and especially rich in EGCG (Epigallocatechin gallate)
Preparation of kombucha tea
- It is basically prepared by fermenting sweetened black tea or green tea with a starter culture
- The starter culture contains symbiotic colony of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY)
- During fermentation process the yeast of SCOBY breaks the sugar of the tea and produces several probiotic bacteria
- It is then carbonated, which is responsible for making the drink fizzy
Biological properties
Antioxidant properties
- It is rich in probiotic, polyphenols and antioxidants, which are accountable for supporting healthy cell functions that help to improve overall health status
- It is associated with preventing the harmful consequences of oxidative stress within body by inhibiting free radicals induced oxidative damages

Anti-inflammatory properties
- The polyphenolic compounds of kombucha tea are considered as the chief compounds responsible for lessening inflammation
- It helps to prevent low grade inflammation as well
- Consumption of kombucha tea is very effective for reducing the susceptibility of developing chronic diseases (like arthritis, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, allergies and respiratory disorders) as it prevents the occurrence of inflammatory events within body
- It is also related with decreasing swelling and pain
Antimicrobial properties
- As mentioned above preparation of kombucha tea requires fermentation and this fermentation process is responsible for producing acetic acid, which exerts potent antimicrobial activities
- It has seen that it helps to inhibit the growth of both gram positive and gram-negative bacteria within host hence reduces the prevalence of developing various infectious diseases
Anti-carcinogenic properties
- Polyphenols, antioxidant, Vitamin C, glucuronic acid, gluconic acid and lactic acid components of kombucha tea have strong anti-carcinogenic properties
- Its consumption is very effective for suppressing the growth of malignant cell as it helps to regulate apoptosis and cellular proliferation
- It helps to prevent gene mutation, which helps to decrease the risk of developing cancers as well
- It helps to prevent the growth of tumor cells within body
- It has seen that kombucha plays significant role for inhibiting angiogenesis (growth of new blood vessels), which especially helps to reduce the prevalence of prostate cancers

Health benefits
Role on immunity
- Consumption of kombucha tea is very effective for improving the immunological responses of the body as it contains numerous fermenting bacteria, which help in boosting up the overall defense mechanism
- It is associated with stimulating the synthesis of antibodies that also promotes immunity
Role on mental health
- It has seen that consumption of kombucha tea (probiotic enriched beverages) is very useful for decreasing depression, anxiety and insomnia
- It is associated with enhancing the secretion of serotonin that helps to prevent the feeling of hopelessness, sadness and also improves mood
Role on digestive health
- As mentioned above it is rich in probiotic and contains various fermenting bacteria, which are associated with improving the load of beneficial intestinal flora that promotes gut health
- It also helps to maintain the balance between good and bad bacteria within gut (gut dysbiosis) that helps in the stabilization of digestive tract
- Its anti-inflammatory activities are responsible for protecting the gastrointestinal tract from inflammatory damages and hence reduces the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease
- Its consumption is also very effective for reducing the prevalence of diarrhoea allied with antibiotic use
- It is also related with decreasing the susceptibility of developing constipation, irritable bowel syndrome and bloating

Role on metabolism
- It helps to boosting up the metabolic processes of the body
- It is associated with increasing the catabolic rate
- Epigallocatechin-3-gallate component of kombucha tea (prepared from green tea) helps to make the metabolic process faster
Role on detoxification
- It helps in detoxification process and helps in toxin elimination from body
- Glucuronic acid of kombucha tea is considered as the main detoxifying agent that helps to convert the harmful toxins of body into excretable substance and facilitates their excretion
- It is also related with preventing the absorption of other toxins within body
Role on weight management
- Kombucha is considered as one of the healthiest drinks, which helps to maintain healthy body weight as it is a low calorie beverages
- As we know that consumption of sweetened tea contributes more calorie if consumed in excess amount as sugar found in tea is high in calorie thus resulting in weight gain. On a contrary, kombucha does not increase the risk of obesity as it contains low sugar
- It has seen that kombucha can easily replace calorie rich beverages or health drinks or fruit juice, which ultimately help to cutting back on sugars resulting in weight reduction

Medicinal usage
Effect on cardiac vascular system
- It is extensively used for enhancing the functionality of heart
- It has seen that its consumption helps to reduce the concentration of bad cholesterol (LDL) within body whereas increases the level of good cholesterol (HDL) that also provides a positive effect on cardiac health
- It helps to prevent fat accumulation within blood vessels thus decreases the susceptibility of developing atherosclerosis and coronary artery diseases
- It also helps to reduce the prevalence of heart attacks and strokes
Effect on hepatic health
- Consumption of kombucha is extremely effective for healthy liver function
- It has seen that it protects the liver from various oxidative as well as inflammatory damages
- It also helps to decrease the prevalence of drug induced liver damage and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Hypoglycemic effect
- It plays significant role in reducing blood sugar concentration by inhibiting the activity of alpha amylase (carbohydrate splitting enzyme) and by increasing insulin secretion
- It mainly helps to reduce the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- It is also very effective for reducing HbA1c level

It acts as an effective remedial action for arthritis as it helps to reduce joint swelling and joint pain (especially knee)
It helps to decrease the risk of developing anaemia as it provides significant amount of iron, which helps in hemoglobin synthesis
It is also used for making the body hydrated
Risk factors
- As kombucha tea is acidic in nature hence its excessive consumption may cause some digestive issues like heart burn, stomach upset, stomach ulcer etc
- It causes metabolic acidosis as well if consumed in large amount hence it is better to consume kombucha moderately
- Over consumption of kombucha is also responsible for breaking down the enamel of teeth (due to its acidic nature) thus it is better to rinse the teeth with simple water after consuming kombucha

Source:
Chakravorty, S., Bhattacharya, S., Bhattacharya, D., Sarkar, S. and Gachhui, R., 2019. Kombucha: a promising functional beverage prepared from tea. In Non-Alcoholic Beverages (pp. 285-327). Woodhead Publishing.
Holbourn, A. and Hurdman, J., 2017. Kombucha: is a cup of tea good for you?. Case Reports, 2017, pp.bcr-2017.
Ivanišová, E., Meňhartová, K., Terentjeva, M., Harangozo, Ľ., Kántor, A. and Kačániová, M., 2019. The evaluation of chemical, antioxidant, antimicrobial and sensory properties of kombucha tea beverage. Journal of Food Science and Technology, pp.1-7.
Kapp, J.M. and Sumner, W., 2019. Kombucha: A systematic review of the empirical evidence of human health benefit. Annals of epidemiology, 30, pp.66-70.
Leal, J.M., Suárez, L.V., Jayabalan, R., Oros, J.H. and Escalante-Aburto, A., 2018. A review on health benefits of kombucha nutritional compounds and metabolites. CyTA-Journal of Food, 16(1), pp.390-399.
Martínez Leal, J., Valenzuela Suárez, L., Jayabalan, R., Huerta Oros, J. and Escalante-Aburto, A., 2018. A review on health benefits of kombucha nutritional compounds and metabolites. CyTA-Journal of Food, 16(1), pp.390-399.
Özdemir, N. and Çon, A.H., 2017. Kombucha and Health. J Heal Sci, 5, pp.244-50.
Villarreal‐Soto, S.A., Beaufort, S., Bouajila, J., Souchard, J.P. and Taillandier, P., 2018. Understanding kombucha tea fermentation: a review. Journal of food science, 83(3), pp.580-588.