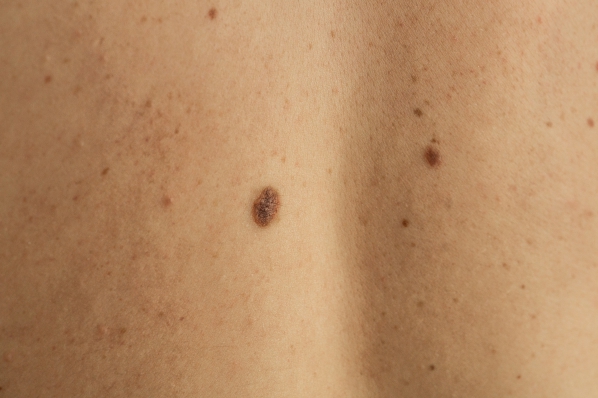
What is melanoma (skin cancer)?
Melanoma, most commonly known as skin cancer, is when cancer arises in the cells found in the skin known as melanocytes. These cells are responsible for the production of melanin which is a pigment that gives your skin its colour. In skin cancer, your melanocytes become abnormal and start to multiply uncontrollably.
Melanoma is the fifth most common cancer in the United States. With time, statistics have shown that the number of cases keep on increasing by an average of 1.5% annually. Melanoma can also arise in other organs such as the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. 10-20% of all melanomas of the skin appear on the head or neck region. The majority develop on the face.
Melanoma can sometimes be very dangerous and should be taken into serious consideration. Treatment should be initiated early to prevent spread of the disease and improve the outcome.
What are the causes and risk factors of melanoma?
The exact cause of melanoma is unknown, however, several factors has shown to be increasing the risk of having the disease. These include:
· Sun exposure: Exposure to ultraviolet-B (UV-B) radiation can significantly increase your risk of having skin cancer. This triggers genetic mutations in melanocytes, resulting into its malignant transformation and multiplication. This explains why melanoma is most commonly present on sun exposed areas.

· Ultraviolet radiation exposure: You may also be exposed to UV radiation from tanning beds and UV-A therapy for other purposes.
· Tendency to burn easily: Some people are more prone to sunburns compares to others. These include people with fair skin, red hair, blue eyes and poor ability to tan. This is because your skin lack melanin, hence you are less protected against UV radiation.
· Freckles and nevi: If you have freckles or nevi, you are more prone to have skin cancer.
· Family history: If you have close family members with skin cancer, you are also more at risk of having the condition.
What are the symptoms of melanoma?
As mentioned earlier, skin cancer can arise anywhere on your body. However, they are more likely to develop on sun exposed areas. Hidden melanomas, that is melanoma arising on body parts that are not exposed to sunlight, are more likely to occur in dark skinned people.
Melanoma usually presents as the development of a new pigmented growth or mole on the skin or as a changing existing mole. You can distinguish between a normal mole and a melanoma based on some characteristic features of the latter. This can be remembered using the letters A to E as follows:

· Asymmetry: The lesion is not symmetrical
· Border: It has an irregular border
· Colour: There may be different colours within the same mole
· Diameter: It is larger than the eraser on the end of a pencil
· Evolution: It can change size, colour or shape with time
How is the diagnosis of melanoma made?
To make the diagnosis of melanoma, your doctor will first begin by asking you a series of questions including:
· When was the lesion first noticed?
· Does anyone in your family have/had skin cancer?
· Have you been excessively exposed to sunlight or tanning beds?
· Have you sustained severe sunburns when you were younger?
· Do you have a condition that lowers your immune system?
 · Have you had prolonged UV-A therapy?
· Have you had prolonged UV-A therapy?
Following a thorough history taking, your doctor will then proceed with a physical examination. He/she will have to examine your entire body for any suspicious lesions. If the diagnosis of melanoma is suspected, your doctor may have to perform a biopsy. In this procedure, your doctor will remove the whole or a small sample from the abnormal area. This is sent for further evaluation in a laboratory where the diagnosis of melanoma can be confirmed.
The stage of the cancer should also be determined as it affects the treatment choice as well as helps in determining the severity and possible outcome.
How is melanoma treated?
The choice of treatment for melanoma will depend on the cancer staging, your age and the presence of other medical conditions. There are several treatment options for skin cancer. Your doctor knows best which treatment modality will be the best fit for you. These include:
· Surgery: The main treatment option for skin cancer is surgery. This involves the complete removal of the lesion. Your doctor will also check the nearby lymph nodes to see whether the cancer has spread to the nodes or to other parts of the body. Lymph nodes are bean-shaped structures in which infection-fighting cells are present.

· Immunotherapy: These medications work by helping your body’s immune system to fight against the growth of the tumour. They can be used after resection of the cancer, if it has spread to other parts of the body or lymph nodes.
· Targeted therapy: These are medications that work on specific proteins present in the cancer. This can also be used after surgery or in cases where the cancer has started to spread.
· Radiation therapy: This treatment involves the use of high energy beams to kill cancer cells. This can be used if the cancer has spread to lymph nodes
· Chemotherapy: This involves the use of medications that can be given intravenously or orally to kill cancer cells.
After treatment for melanoma, it is recommended to regularly check your skin to look for any abnormal changes that may be present.
What are the complications of melanoma?
There are several complications that may arise from melanoma including:
· Rupture of suture site after surgery
· Death of surrounding skin

· Wound infection
· Swelling of the lower and upper extremities
How can melanoma be prevented?
The main step in the prevention of skin cancer is to protect yourself from sun rays. The following measures can be taken to reduce your risk of having melanoma:
· Avoid exposure to the sun from 10 AM to 4 PM
· Wear sunscreen each time you are going out and reapply as often as necessary
· Wear wide-brimmed hats, long-sleeved shirt and long pants
· Do not use tanning beds
The above measures and particularly recommended if you are at a higher risk of having melanoma.
Prognosis of melanoma
The prognosis of skin cancer depends on the following factors:
· Thickness of the lesion: the prognosis is worse with thicker tumours
· Spread of the cancer into lymph nodes
· Spread of the cancer into other organs

· Presence of ulceration on the lesion
· Location of the tumour- lesions found on the face or trunk have poorer prognosis compared to those found on extremities
· Being a male is associated with a poorer prognosis
5-year survival rates decrease with more advanced stages. Early detection of the cancer and prompt initiation of treatment can improve the outcome of the disease.

Source:
Tan, W., 2020. Melanoma: Practice Essentials, Overview, Indications And Guidelines.
Tan, W., 2020. Skin Cancer - Melanoma: Overview, Diagnosis, Treatment & Management.
Swetter, S., 2020. Melanoma: Clinical Features And Diagnosis.