What is menopause?
Menopause is a normal phase through which every women go through at around 45-55 years old. It is when a women no longer has her menstrual periods for a full period of 12 months which cannot be attributed to any other disease or imbalance. It is also characterized by the cessation of ovulation. If menopause occurs in women younger than 40 years old, it is considered as abnormal and may be due to some underlying pathologies. A woman can no longer fall pregnant following menopause.
Menopause is not a process that occurs suddenly. The changes towards menopause start several years before. Some changes in the menstrual cycles may be noticed as well as other menopausal symptoms. It should be pointed out that menopause is a completely normal process and does not always have to be treated. However, if the symptoms start to be bothersome, some treatments are available to improve your quality of life.
What are the causes of menopause?
Most of the time, menopause is a completely normal process which occurs following a decline in reproductive hormones with increasing age. These hormones include Estrogen and progesterone. The function of these hormones is to regulate menstruation. This inevitably leads to a decline in fertility and changes in your menstrual cycle.
However, there may be some other factors that can lead to premature menopause. These include:

- Surgery: In some cases, where disease affects your ovaries, surgery had to be done to remove them. This surgical procedure is known as oophorectomy. Your ovaries are responsible for the secretion of Estrogen and progesterone. Hence, removal of both ovaries will ultimately result in premature menopause.
- Primary ovarian insufficiency: This is the main cause of menopause before 40 years old. This occurs when your ovaries fail in maintaining the normal levels of reproductive hormones in your body. There may be genetic or autoimmune causes behind this process. However, in most cases, no underlying cause may be found.
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy: These strong treatments are usually used in cancer management. These can cause a decline in the function of ovaries. This is especially true if radiation therapy is targeted directly on the ovaries.
What are the changes that occurs during menopause?
Changes that are associated with menopause can start 3-4 years prior to definitive menopause. This phase is also known as the menopausal transition or perimenopause. With increasing age there are fluctuations in the levels of reproductive hormones in a woman.
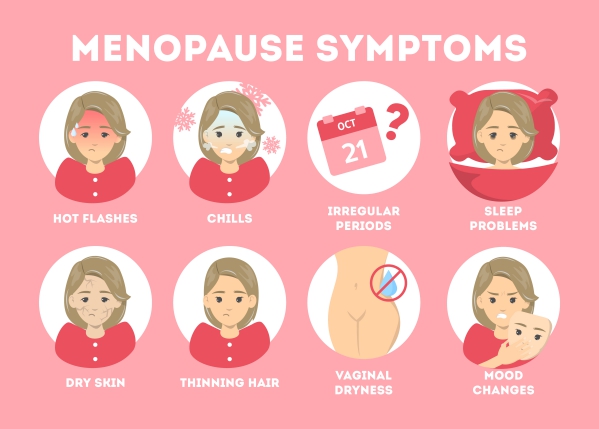
Perimenopause and menopause may manifest with the following symptoms:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Bleeding lasting for fewer days than before
- Hot flashes
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood symptoms
- Dryness of the vagina
- Spotting between periods

Hot flashes are usually felt as sudden feelings of heat on the face and the upper chest that may spread all through the body. These may be accompanied by sweating, shivering, anxiety and palpitations.
Night sweats are basically hot flashes occurring at night. These can also prevent you from sleeping as you may be feeling too hot or cold. They can happen several times per night. Several complications may arise from night sweats including fatigue, irritability, poor concentration and mood swings.
Vaginal dryness arise due to a decrease in Estrogen which is responsible for adequate production of your natural lubricant in your vagina. This can result into painful sexual intercourse, discomfort and itching.
Mood changes can also be significant among premenopausal and menopausal women. Some women may constantly feel sad, have difficulty concentrating, lose interest in previously enjoyable activities and have sleep problems.
How is the diagnosis of menopause made?
The diagnosis of menopause is usually made clinically, that is, only from a good history taking and physical examination. In some rare cases, further tests may be required. There is no specific test done to make the diagnosis of menopause. However, some tests may be needed to look for the underlying cause in some rare cases. These tests may include:
 Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) which is usually elevated in menopause
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) which is usually elevated in menopause- Estrogen (Estradiol) which is usually low in menopause
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to rule out hypothyroidism which may mimic symptoms of menopause
How is menopause managed?
The majority of time, menopause does not require any treatment as it is a completely normal process. However, in some cases, the symptoms may be too bothersome and therefore treatment may be initiated to improve your quality of life. Treatment options may include the following:
- Hormonal therapy: Medications containing a combination of Estrogen and progesterone may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of menopause. Estrogen is effective for the treatment of hot flashes. The medications are also effective in alleviating vaginal dryness and mood disturbances. These medications are available in the form of pills, skin patches, vaginal rings, gels, creams or sprays. They should be initiated before the age of 60 and are not given for more than 5 years. However, these drugs are not recommended in women who have a history of breast cancer, heart diseases or stroke.
- Non-estrogen treatments: There are a variety of non-estrogen medications that can be used to treat hot flashes. These include paroxetine, gabapentin, antidepressants, oxybutynin and injectable progesterone. However, none are as effective as estrogen therapies.
- Plant-derived estrogen: These are also known as phytoestrogens. They are considered as safer alternatives to hormonal therapies. Phytoestrogens can be found in a variety of food products including soybeans, chickpeas, lentils, flaxseed, lentils, grains, fruits, vegetables, and red clover. Similarly, women with a history of breast cancer should avoid the above foods.

What are the complications associated with menopause?
The decline in hormones in your body can contribute in the development of various complications. These complications include:
- Osteoporosis: This is a condition in which the bones in your body become thin and fragile. This make you more prone to fractures in your spine, hips and wrists.
- Decline in sexual function: Vaginal dryness and decrease in sexual drive is due to a decrease in reproductive hormones. Sexual intercourse becomes painful and is often associated with bleeding.
- Weight gain: This is common during menopause as there is a decrease in your metabolism.
- Cardiovascular disease: Decrease in estrogen levels make you more prone to having heart diseases.

Source:
Coney, P., 2018. Menopause: Practice Essentials, Overview, Physiology.
Casper, R., 2020. Clinical Manifestations And Diagnosis Of Menopause.
Martin, K., 2020. Treatment Of Menopausal Symptoms With Hormone Therapy.


