Phosphorus is a naturally occurring micronutrient (mineral) of great health significance. It is essentially required for performing some biological reactions through phosphorylation process which include cell signaling, ATP synthesis and bone mineralization. It is generally present in natural food stuffs as well as in several supplements. It also found in human body and primarily present in bone in the form of calcium phosphate. It is one of the most important structural constituent of cell membranes and nucleic acids and associated with maintaining their proper functions. Phosphorus is essentially required by every living organism for their survival. So, it should be consumed daily as per recommended allowance to avoid undue health hazards.
Some important facts which should be known regarding phosphorus
- Phosphorus is the second most abundant mineral (next to calcium) found in body. Human body contain about 1 kg of phosphorus, among which about 80% of phosphorus is present in bone and teeth, combines with calcium, about 10% is present in blood, muscle and in some organic substance of body like carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Remaining 10% is symmetrically distributed in various chemical compounds of body
- It has found that phosphorus obtained from animal sources is better absorbed than those obtained from plants or other sources. Phosphorus can only perform its function adequately when it is well absorbed. It is generally absorbed through jejunum. Calcitriol helps in phosphorus absorption by enhancing its uptake along with calcium
- When the dietary ratio of calcium and phosphorus is ranging between 1:2 and 2:1 then its absorption reaches to its optimum level
- Phosphorus in an electrolyte of body which has a negative charge and helps to regulate the acid base balance and homeostasis of the body
- Normal level of phosphorus in plasma is 2.54 to 4.5 mg per dl and it should be maintained to avoid harmful consequences

Sources
- Food stuffs rich is phosphorus include, milk and dairy products, meat, fishes, sea foods, poultries (mainly turkey and chicken), whole grain cereals, nuts, beans, lentils, oatmeal, sunflower seeds, garlic, potatoes, dried foods. All of these are the natural sources of phosphorus
- Phosphorus also found in some foods as preservatives for enhancing their shelf life. These preservatives include: Phosphoric acid, monosodium phosphate, disodium phosphate, tri-sodium phosphate, tetra sodium phosphate and di-calcium phosphate
- Phosphorus can also be obtained by consuming its supplements, but it is always beneficial to consume phosphorus from natural sources than any other sources. The dietary supplements of phosphorus can only be consumed if an individual cannot take it through natural sources

Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for phosphorus
- Recommendation of phosphorus for adult male and female is 700mg per day which is required to fulfill the body’s demand during adulthood
- 100mg of phosphorus should be given to infants between six months of age and about 275mg should be given to infants between the age group of six to twelve months
- Children between the age group of 1 to 8 years should consume about 460mg to 500mg of phosphorus daily
- The need of phosphorus is increased in many folds during adolescence period for supporting the accelerated growth. About 1250mg of phosphorus is required daily to fulfill the increased demand of the body

Health benefits
Effect on bones and teeth
- Phosphorus helps in the formation, growth and development of bones and teeth
- Phosphorus binds with calcium and forms calcium phosphate which is the main structural component of bone as well as teeth
- Phosphorus along with calcium and Vitamin D help to improve the mass and density of bones and hence help to make bones more healthy and stronger
Effect on nucleic acid
- Nucleic acid is an important organic substance, composed of several nucleotides and present in every cells of living organism. DNA and RNA are the examples of nucleic acid
- Phosphorus is an important integral part of nucleotides and helps to synthesize DNA and RNA which are necessary for storing and transmitting genetic information
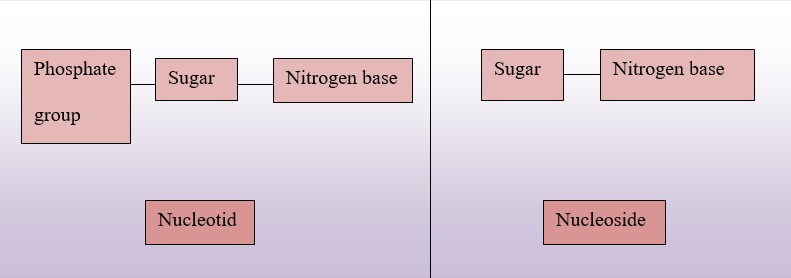
- Every nucleotide is made up of a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, nitrogen bases (purine or pyrimidine) and a phosphate group, without phosphate group the molecule is termed as nucleoside (containing only sugar and nitrogen bases)

- Nucleotides act as monomers and several nucleotides are bind with each other and form a polymer known as nucleic acid (DNA and RNA)
Effect on cell membrane
- Phosphorus is a vital component of cell membrane
- Basically, the cell membrane is composed of three layers which include lipid, protein and lipid, where proteins are embedded between two layers of lipid
- The lipids present in cell membrane are phospholipids (phosphate group is attached with triglyceride) which is known as lecithin and it is the only substance responsible for the permeability of cellular membrane
- Structurally phospholipids have a polar head and a non-polar tail. This phenomenon is responsible for cellular transport, and makes the cell membrane dynamic which is very essential for cellular survival
Effects on synthesizing high energy phosphate compound
- Phosphorus plays several essential roles in various metabolic reactions where it helps to synthesize high energy compound like ATP and GTP. These compounds are responsible for providing energy
- It helps in the synthesis, utilization and storage of energy within body
Other benefits
- It helps in muscle contraction and helps to recover muscle injuries
- It is associated with conducting nerve impulse adequately throughout the body and helps to coordinate the entire body’s system
- It supports normal heart rhythm
- It helps the kidney to filter and excrete waste properly

Risk factors
- It is very important to maintain the balance of phosphorus within body. About 700mg of phosphorus is excreted through kidney daily which is equal to its daily intestinal absorption. So, if it is not consumed as per its daily requirements then it would develop hypophosphatemia (low phosphate level). It is responsible for bone pain, fractures, muscle weakness, seizures and in severe condition causes respiratory failure
- People, who suffer from hypothyroidism, Vitamin D deficiency, Cushing’s syndrome, parathyroid disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sepsis or people in severe trauma (like burn) or alcoholics are more susceptible to develop phosphorus deficiency
- Phosphorus supplements are also used to overcome its deficiency, but it should be consumed carefully (as per physician recommendation). Excessive consumption of supplement is responsible for developing several complications such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache, dizziness. It often causes allergies which are characterized by rashes on skin, swelling of face and tongue after immediate consumption of supplements, shortness in breath and rapid heartbeat. Though development of phosphorus allergy is very rare but if anyone experiences the above-mentioned complications should consult with physician as early as possible otherwise it would become very fatal
- On a contrary, excess phosphorus intake from natural source cannot cause toxicity as phosphorus can be excreted through urine and too some extent in stool. Whereas it has shown that excess phosphorus is beneficial for those individuals who suffer from osteoporosis, as it helps to increase the bone mass density, which is associated with preventing osteoporosis

Source:
Bhandari, S.K., Liu, I.L.A., Kujubu, D.A., Huynh, T., Behayaa, H., Kovesdy, C.P., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Jacobsen, S.J. and Sim, J.J., 2017. Use of phosphorus binders among non-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients and mortality outcomes. American journal of nephrology, 45(5), pp.431-441.
Chen, L., Tian, F. and Sun, Z., 2016. Phosphorus nutrition and health: utilization of phytase-producing Bifidobacteria in food industry. Probiotics and Prebiotics in Human Nutrition and Health, 1(1), p.266.
Goodson, J.M., Shi, P. and Razzaque, M.S., 2019. Dietary phosphorus enhances inflammatory response: A study of human gingivitis. The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology, 188, pp.166-171.
Lamberg-Allardt, C. and Kemi, V., 2017. Interaction Between Calcium and Phosphorus and the Relationship to Bone Health. In Clinical Aspects of Natural and Added Phosphorus in Foods (pp. 145-157). Springer, New York, NY.
Pasek, M., 2019. A role for phosphorus redox in emerging and modern biochemistry. Current opinion in chemical biology, 49, pp.53-58.
Tonini, D., Saveyn, H.G. and Huygens, D., 2019. Environmental and health co-benefits for advanced phosphorus recovery. Nature Sustainability, 2(11), pp.1051-1061.
van Dronkelaar, C., van Velzen, A., Abdelrazek, M., van der Steen, A., Weijs, P.J. and Tieland, M., 2018. Minerals and sarcopenia; the role of calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, sodium, and zinc on muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical performance in older adults: a systematic review. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 19(1), pp.6-11.
Vorland, C.J., Stremke, E.R., Moorthi, R.N. and Gallant, K.M.H., 2017. Effects of excessive dietary phosphorus intake on bone health. Current osteoporosis reports, 15(5), pp.473-482.