Parenteral nutrition, administration of absorbale form of nutrients, indications and TPN formula
Description : Parenteral nutrition is a special feeding technique through which all essential nutrients with
Article Details :
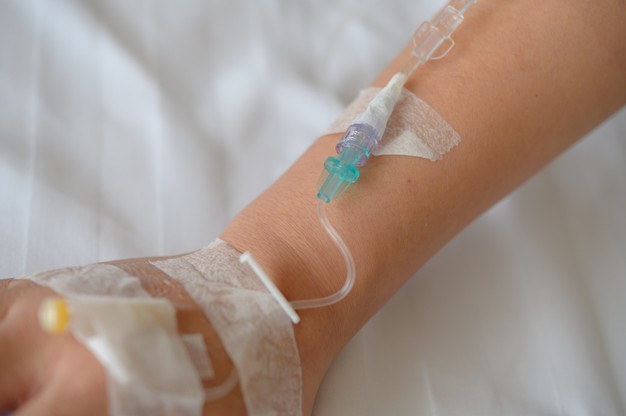
Parenteral nutrition is a special feeding technique through which all essential nutrients with required amount are provided directly into the vein of a patient. It is basically dealt with the intravenous administration of isotonic or hypertonic solutions of nutrients via VAD (venous access device) straight into the intravascular fluid for providing proper nutrients to the patient, who is not able to receive optimum nutrition through GI tract.
Types of parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition is of four types, which include –
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
It helps to provide all nutrients as per the body’s need through parenteral route. It mainly uses the central vein for administration purpose
Peripheral parenteral nutrition
In this type of parenteral nutrition the nutrients are given through peripheral vein to the patient
Hyperalimentation
In this type of parenteral nutrition, 150% of daily requirements are provided to a patient through parenteral route to generate a positive nitrogen balance for gaining weight
Partial parenteral nutrition
In this type of parenteral feeding, 30 to 50% of daily nutrients requirements are provided through parenteral route, whereas rest portions are provided through enteral route (through tube feeding)
Significance
- It helps to fulfill the need of sick individuals
- It especially helps to provide foods to those individuals, who are unable to chew and swallow
- It mainly helps to bypass the gastrointestinal tract for the patients who are not able to take food orally
- It helps to repair damages
- It mainly helps to meet the need of calories
- It helps to maintain the ability of the body to metabolize nutrients
- It also helps to correct all deficiencies of the body and promotes well being
- It contains all the nutrients in absorbable form as it is administered directly into vein hence the nutrients are readily absorbed and entirely utilized for metabolism
Indications
Cases, which require parenteral nutrition, are listed below –
- When gastrointestinal tract stops functioning
- Major gastrointestinal surgery
- Acute pancreatitis
- Gastro intestinal fistula
- Small bowel ischemia
- Malnutrition (especially which is manifested with 10 to 15% weight reduction)
- Short bowel syndrome
- Malabsorption
- Multi organ system failure
- Intestinal obstruction
- Paralytic ileus
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Persistent vomiting
- Severe diarrhoea
- Acute renal failure
- Liver failure
- Tumor in gastrointestinal tract
- Multiple fractures
- Severe burns
- NPO (more than 5 days)
- Metastatic cancer
Composition of parenteral nutrition
Parenteral nutrition provides a combination of fluid, sugar, trace elements, amino acids, electrolytes, vitamins and fats. Generally the nutrients that are present in parenteral formula are listed below –
Carbohydrates
It generally contains glucose (the end product of carbohydrate digestion) and dextrose monohydrate
Proteins
It contains amino acids, especially crystalline amino acids
Fats
It mainly contains emulsified fat. Generally 10% and 20% of fat emulsions are used. It has seen that 10% emulsions are responsible for providing 1.1 kcal per ml whereas 20% emulsions are accountable for providing 2 kcal per ml
Vitamins
It contains all the essential vitamins and especially rich in Vitamin B9 or folic acid, Vitamin B12 and Vitamin K
Minerals
It basically contains copper, zinc, iodine, chromium and magnesium
Water
Water is the main constituent of parenteral nutrition and about 30 to 50 ml of fluid per kg of ideal body weight is required to prepare parenteral formula
Electrolytes
It basically contains sodium, potassium, chlorine, calcium and phosphorus

Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) formula for children
Calories
- It provides 110 to 125 kcal of energy per kg of ideal body weight per day to new born
- Whereas, TPN for older child is associated with providing 100 to 110 kcal of energy Read more