Thyroid cancer, Thyroid disorder, Papillary, Follicular, Anaplastic, Medullary, Thyroidectomy
Description : The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland that in located in the neck area. It is responsible to
Article Details :
What is thyroid cancer?
The thyroid is a butterfly shaped gland that in located in the neck area. It is responsible to release hormones that carry out a variety of functions in the body. Some of these functions include regulation of the heart rate, pressure of blood, body temperature and weight. The hormones produced by the thyroid gland are triiodothyronine, thyroxine and calcitonin. In order to secrete these hormones, the brain has to produce another hormone first, known as the thyroid-stimulating hormone which will stimulate the thyroid gland.
When a cancer develops in the thyroid gland, it may not cause any symptoms at first. However, with time, as the cancer grows and develops, it may start to cause pain and swelling as well as other symptoms. There are several types of thyroid cancers namely: papillary carcinoma, follicular carcinoma, medullary thyroid carcinoma and anaplastic carcinoma amongst others. They vary in their rate of growth and aggressiveness. However, most of them can be cured with treatment and surgery.
Thyroid cancers represent around 1% of all new cancers diagnoses in the United States. Approximately 23,500 cases of thyroid cancers are diagnosed every year. They are usually more common in women compared to men. It is also most common in the 3rd and 4th decades of life.
What are the types of thyroid cancers?
Thyroid cancers are classified based on the type of cells present in the tumour. In order to known which type of tumour a person has, a sample of tissue from the tumour needs to be collected and examined under a microscope. The types of thyroid cancers include the following:
- Papillary thyroid cancer: This is the most common type (80%) and it arises from particular cells known as the follicular cells. It is a type of thyroid cancer that can occur at any age, however, its peak incidence is among people aged between 30-50 years.
- Follicular thyroid cancer: Similarly, follicular cancer also arises from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. This is most common in older people.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer: This is the rarest type of cancer affecting the thyroid. However, it is the most aggressive type as it grows rapidly and most often is very difficult to treat.
- Medullary thyroid cancer: This is a type of cancer that affects cells known as C cells that release calcitonin. It is often associated with other diseases as genetic syndromes.
What are the causes of thyroid cancer?
The exact cause of thyroid cancer is not known. A cancer usually arises when cells in an organ or tissue start to multiply uncontrollably due to some underlying genetic mutations that occur in certain cells. The cells lose the ability to die as any other normal cell would do. As the cells continue to grow and multiply, they accumulate forming a tumour. This tumour can further grow and invade surrounding parts of the body.
What are the risk factors for thyroid cancer?
The following factors increases your risk of having thyroid cancer:
- Being a female
- Being exposed to high levels of radiation especially in the head region (as therapies in the cases of other cancers)
- Genetic predispositions
What are the signs and symptoms of thyroid cancer?
When the tumour is at its early stages, there may not be any apparent signs or symptoms. However, with time, the tumour progresses in size and this may result in the appearance of various symptoms. These include:
- Presence of a lump on the neck that can be palpated usually painless
- Hoarseness of voice
- Dysphagia also known as difficulty swallowing
- Neck pain
- Throat pain
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Heat intolerance
- Palpitations
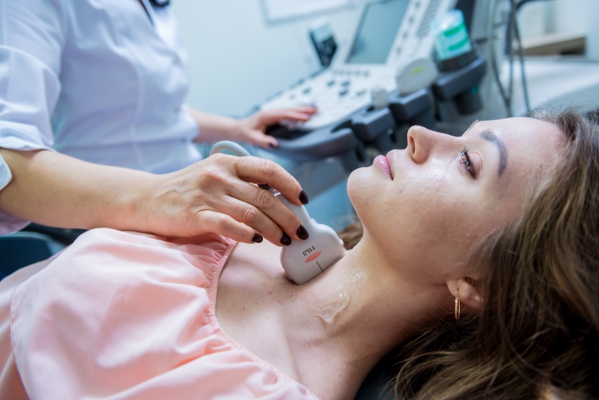
How is the diagnosis of thyroid cancers made?
To make the diagnosis of thyroid cancers, your doctor will first begin to ask you a series of questions to know more about your symptoms. He/she will then proceed with a full physical examination to look for signs of thyroid cancer. In most cases, your doctor will order further tests to confirm the diagnosis. These include:
- Blood tests: Blood tests can be done to check for the levels of thyroid hormones present in the blood. This is known as thyroid function tests.
- Ultrasound: This is an imaging technique that uses sound waves emitted by a transducer to create images of organs. This allows the identification of nodules in the thyroid gland.
- Biopsy: In this procedure, a sample of the nodule identified is collected using a special needle. This sample is then sent to the laboratory to be examined under the microscope. If cancer cells are identified, the diagnosis of thyroid cancer is confirmed.
How is thyroid cancer treated?
Once the diagnosis is established, your doctor will evaluate the extent of the disease. The cancer will then be staged and treatment initiated accordingly. Treatment options may include the following:
- Watch and wait: If the cancer is very small and has a low Read more