Beer is a popular alcoholic beverage widely consumed throughout the world. Beer is produced by fermenting barley and malt. Generally, yeast is used for the fermentation process which helps to ferment the sugar contents of barley and malt and converts them into alcohol.
Consumption of beer is comparatively better than consuming other alcoholic beverages as beer contains negligible fat and cholesterol compared to others and contains various important phytochemicals and antioxidants, which have significant health importance.
Nutritional profile
- Beer provides significant number of calories on its oxidation and excessive consumption of beer may leads to weight gain. According to the calorific value, beer is categorized into three types which include – light beer or beer under 100 calories (like Michelob Ultra beer, Beck's Premier Light beer etc.), beer under 150 calories (Coors Light, Bud Light beer, Beck's beer etc.) and high calorie beer (Michelob lager, Blue Moon Belgian White beer etc.)
- Barley and malt of beer contributes for carbohydrate
- Beer does not contain any fat or cholesterol
- It contains too some extent of proteins
- It also contains several vitamins especially Vitamin B complex (folic acid, biotin and niacin)
- It is rich in various trace elements that include calcium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium and magnesium
- It contains about 11 to 13.9g of alcohol especially ethanol
- It also contains several phytonutrients, which are responsible for exerting antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and cardio protective effects. These include phenolic acid, flavanols, proanthocyanidins, hydroxycoumarins and xanthohumol

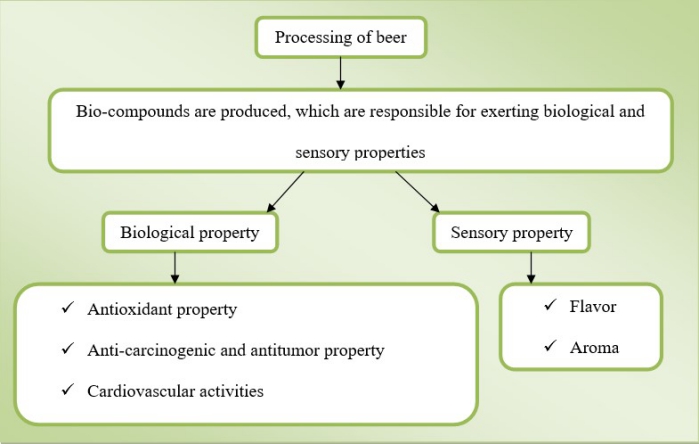
Biological and sensory property
- Processing of beer involves fermentation, which helps to produce several phenolic and volatile compounds that are responsible for exerting various organoleptic characteristics of beer
- Bio-compounds present in beer (flavonoids, phenolics and volatiles) have several biological as well as sensory properties
- Biological properties include antioxidant, cardio protective and anti-carcinogenic activities of beer. It helps to prevent oxidative damages of body, protects cardiovascular system, reduces the growth of tumors and suppresses malignant cell growth
- Xanthohumol component of beer is principally responsible for exerting its functional characteristics, which include aroma and flavor. It is also accountable for the bitterness of beer with a flavor of hop
Health benefits
Role on cardiovascular system
- Beer is considered as an important cardio protective beverage
- It helps to improve the concentration of HDL in body and reduces the oxidation of LDL that helps to prevent atherosclerosis
- Consumption of beer is associated with providing a thinning effect on blood and prevents clot formation within blood vessels that helps to reduce the risk of developing coronary artery diseases
- Individual who consume beer in moderate amount have lesser risk of experiencing heart attacks or strokes
- It has also seen that consumption of beer is related with reducing the risk of congestive heart failure

Role on GI tract
- It has seen that consumption of beer promotes digestion
- It also helps to promote bowel health
- It helps to prevent the susceptibility of developing peptic ulcer by inhibiting the growth of Helicobacter pylori (one of the important causes of peptic ulcer)
Role on stress management
- Beer helps to reduce the stress level and helps to refresh the mood
- It has seen that consumption of beer is associated with increasing the secretion of dopamine, which provides a relaxed and calmer feeling, that helps to reduce anxiety and promotes good sleep
Antimicrobial activities
- The alcohol component (ethyl alcohol or ethanol) of beer exerts strong antimicrobial activity. It helps in complete destruction of microbial cells by denaturing their cellular protein and by lysing their cell membrane
- The hops flavonoid components and antioxidant components of beer also help to prevent the growth and reproduction of microbes within host
Antioxidant and anti-carcinogenic activity
- Polyphenol components of beer especially xanthohumol provide strong antioxidant effects and help to reduce the concentration of free radicals and regulates the level of ROS, which is related with decreasing oxidative damages of body
- Consumption of beer in moderate amount is beneficial to reduce the risk of developing malignant tumors and suppress malignant cell growth. It has seen that it significantly helps to reduce the prevalence of brain, esophageal, colorectal, neck, breast and liver carcinoma

Role on mental health
- The antioxidant and polyphenol components of beer are responsible for preventing oxidative damage of brain cells and promotes the functionality of brain
- Xanthohumol is an important flavonoid of beer helps to prevent degradation of memory
- Consuming beer in moderate amount is associated with improving the ability of performing tasks (mental and physical) and cognitive functions
- It has seen that consumption of beer helps to improve the symptoms of dementia, Alzheimer’s diseases and Parkinson’s disease
Role on eyesight
- Beer helps to improve vision
- The antioxidant components of beer are accountable for preventing oxidative damages of eye
- It also helps to reduce the susceptibility of developing cataract
Role on renal health
- Beer contains significant amount of magnesium and potassium which help to prevent the susceptibility of renal stone formation
- Another important feature of beer is that it is liquid in nature and almost contains 90% of water. Water is an important tool accountable for preventing kidney stone
- Hops of beer are considered as renal health promoting phytochemical. So consuming beer in moderate amount is beneficial for promoting renal health

Role on minimizing diabetes
- Consumption of beer in moderate amount may help to reduce the prevalence of diabetes mellitus (type 2)
- It has seen that diabetic individual who consume beer (moderately) have experienced lesser risk of developing coronary heart disease than non-drinkers

Role on bone health
- The calcium and silicone component of beer help in the growth of the bone and enhance bone density
- They are also associated with reducing the bone losses and help to prevent the prevalence of bone disorders like osteoporosis, osteomalacia
- Moderate alcohol consumption is related with strengthen the bone
Application of beer
Beer can be used in several ways, which include –
- It can be added with chili for improving flavor
- Often beer bath can be taken, it helps to clean and soften the skin and helps to enhance the shine of the hair
- Beer foot bath can also be taken
- It can be used as an effective stain remover
- Beer can be added to meat for marinating, as it helps to make the meat soft

Risk factors
- Pregnant and lactating women should strictly avoid beer consumption
- Individuals suffer from asthma should avoid beer as its consumption may enhances the harmful consequences of asthma
- Individuals suffer from gout should also avoid beer consumption
- It is safe to consume beer in moderate amount. Excessive consumption of beer may develop several health hazards like –
-Trouble in breathing
-Obesity
-Hypothermia
-Diarrhea
-Nausea
-Vomiting
-Black out
-Irregular heart beats
-Hypoglycemia
-Trouble in controlling emotion

Source:
De Gaetano, G., Costanzo, S., Di Castelnuovo, A., Badimon, L., Bejko, D., Alkerwi, A.A., Chiva-Blanch, G., Estruch, R., La Vecchia, C., Panico, S. and Pounis, G., 2016. Effects of moderate beer consumption on health and disease: A consensus document. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, 26(6), pp.443-467.
Elrod, S.M., 2018. Xanthohumol and the Medicinal Benefits of Beer. In Polyphenols: Mechanisms of Action in Human Health and Disease (pp. 19-32). Academic Press.
Humia, B.V., Santos, K.S., Barbosa, A.M., Sawata, M., Mendonça, M.D.C. and Padilha, F.F., 2019. Beer molecules and its sensory and biological properties: a review. Molecules, 24(8), p.1568.
McCullough, M.P. and Volpe, R., 2017. Can Beer Consumption be Part of a Healthy Diet?. Choices, 32(3), pp.1-7.
Nogueira, L.C., do Rio, R.F., Lollo, P.C. and Ferreira, I.M., 2017. Moderate alcoholic beer consumption: the effects on the lipid profile and insulin sensitivity of adult men. Journal of food science, 82(7), pp.1720-1725.
Redondo, N., Nova, E., Díaz-Prieto, L.E. and Marcos, A., 2018. Effects of moderate beer consumption on health. Nutricion hospitalaria, 35(6), pp.41-44.
Sánchez-Muniz, F.J., Macho-González, A., Garcimartín, A., Santos-López, J.A., Benedí, J., Bastida, S. and González-Muñoz, M.J., 2019. The nutritional components of beer and its relationship with neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients, 11(7), p.1558.
Spaggiari, G., Cignarelli, A., Sansone, A., Baldi, M. and Santi, D., 2020. To beer or not to beer: A meta-analysis of the effects of beer consumption on cardiovascular health. PloS one, 15(6), p.e0233619.




