Allergic rhinitis, Hay fever, Allergens, Allergic reaction
Description : Allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is caused by an allergic reaction to allergens, such as
Article Details :
What is allergic rhinitis?
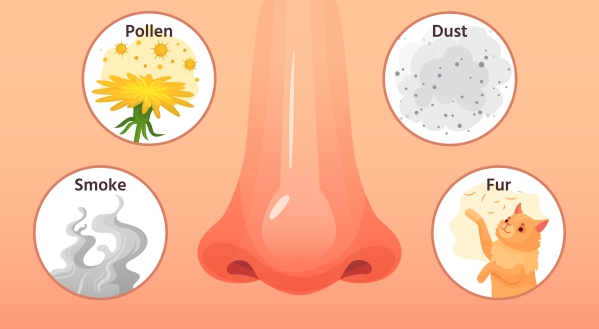
Allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is caused by an allergic reaction to allergens (harmless substance that triggers an allergic response) such as dust mites, pollen and animal fur. It causes cold-like symptoms such as runny nose, itchy eyes and sneezing.
According to the National Center for Biotechnology (NCBI), at least 15% of US citizens suffer from allergic rhinitis. In addition, the most common allergen in seasonal hay fever is pollen.
Causes of allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis develops when your immune system perceives harmless particles in the air (allergens) as harmful. Upon identification of these allergens, your body will produce antibodies against them and the next time your immune system encounters the same allergen it will trigger an allergic reaction. This leads to the release of histamine (natural chemical that defends your body against an allergen and has a central role as mediator of itching) into your blood causing the signs and symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Examples of allergens are mould (a type of fungus), animal fur, dust mites, cat saliva and grass pollen.
Risk factors
The list below consist of factors that may increase your risk of developing allergic rhinitis:
- Humidity
- Having other allergies
- Suffering from asthma
- Cold temperatures
- Having a close relative (parent or sibling) with allergies or asthma
- Cigarette smoke
- Suffering from eczema (the most common type being atopic dermatitis)
- Perfumes
- Having a working environment which exposes you to allergens
- Fumes
- Maternal smoking exposure in the first year of life
- Hairspray
- Air pollution
Signs and symptoms of allergic rhinitis
The list below includes the signs and symptoms of allergic rhinitis:
- Runny nose
- Stuffy nose
- Itchy, watery and red eyes
- Cough
- Hives (red and itchy skin)
- Sneezing
- Itchy nose
- Allergic shiners (blue-coloured skin under the eyes)
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Sore throat
If you are frequently exposed to allergens, with time you will experience symptoms even with a lesser amount of allergen. This is because there will be an accumulation of circulating antibodies in our body.
Furthermore, allergic rhinitis is associated with several other conditions such as:
- Allergic conjunctivitis (up to 60% of patients): itchy, watery and red eyes. The symptoms are usually present on both sides.
- Sinusitis: obstruction of the nasal passage can predispose to sinusitis as bacteria can travel to the sinuses (80% of patients will eventually end up with chronic bacterial sinusitis). The symptoms include stuffy and runny nose with yellow discharge, cough and facial pain.
- Asthma: up to 50% of people suffering from asthma also have allergic rhinitis and the symptoms are cough and chest tightness.
- Food allergy: usually after eating uncooked food such as fruits and vegetables, there will be itching of the mouth and throat immediately.
Allergic rhinitis is different from common cold. There is no fever associated with allergic rhinitis and symptoms appear immediately after exposure to the allergen whereas in common cold there is fever and it takes up to 3 days to experience symptoms.
Making a diagnosis
To diagnose allergic rhinitis, your doctor will perform a physical examination and certain tests such as skin prick test and radioallergosorbent test (RAST). The skin prick test is the most common test whereby your doctor places different substances on your skin to see if there is any allergic response and RAST indicates the amount of antibodies (immunoglobulin E) in your bloodstream.
Treatment
Allergic rhinitis can be treated in mainly 2 ways, namely medications and home remedies:
Antihistamines
This group of drugs work by blocking the effects of histamine. Some examples are:
- Diphenhydramine
- Cetirizine
- Loratadine
Decongestants
Decongestant are not to be used for long periods of time as it can cause a rebound effect. This means that as soon as you stop taking the medication, your symptoms will deteriorate. This class of drug includes:
- Phenylephrine
- Cetirizine with pseudoephedrine
- Oxymetazoline
Decongestants are to be used with caution if you have the following conditions:
- Heart problems
- Previous strokes
- Sleep problems and anxiety
- Elevated blood pressure
- Bladder problems
Eye drops and nasal spray
These medications can be used to alleviate your allergy-related symptoms and itchiness. Like decongestants they should not be used for long periods of time as they can Read more