Ovarian cancer, Ovaries, Gynecological cancer
Description : Ovarian cancer is cancer arising in the female reproductive system, more specifically in the
Article Details :
What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is cancer arising in the female reproductive system, more specifically in the ovaries. The ovaries are a pair of egg-shaped organs found on each side of the uterus and whose function is to secrete hormones, protect females’ eggs and release them for potential fertilization. They are connected to the fallopian tubes through which the eggs travels towards the uterus. In ovarian cancer, the cells present in the ovaries grow out of control and change into abnormal cells.
Ovarian cancer is the most common cause of death from cancer originating in female reproductive organs in the United States. Ovarian cancer may be originating in the ovaries themselves (primary lesions) or may originate from a cancer located somewhere else in the body (secondary lesions). Women aged between 50-65 years are most commonly affected. However, it can occur in women of any age.
It is important to make the diagnosis of ovarian cancer the earlier possible to improve the outcome. There are several treatment options available for ovarian cancer.
What are the causes and risk factors for ovarian cancer?
In ovarian cancer, cells present in your ovaries become abnormal and start to divide uncontrollably. The exact cause for this change is currently unknown. However, it can be caused by mutations in cells that trigger this change.
The following factors can influence the risk of having ovarian cancer:
· Number of children you have: Your risk of having ovarian cancer is higher if you have never had children before. Those who have been pregnant have 50% less risk of ending up with ovarian cancer. You are even more protected against the disease if you had multiple pregnancies.
· Use of oral contraceptives: The use of oral contraceptives has been associated with a decreased risk of having ovarian cancer.
· Family history: You are more at risk of having ovarian cancer if you have a close family member with the same condition.
· History of breast cancer: Women with a history of breast cancer are at higher risk of having ovarian cancer.
· Hormone therapy: Studies have shown that women who are on hormonal therapy are more likely to have ovarian cancer.
· Obesity: Obesity can increase the risk of having ovarian cancer.
· Endometriosis: If you have endometriosis, you are at high risk of having ovarian cancer.
· Use of talcum powder on genitals: Studies have proven that using talcum powder on the vulva can increase the risk of having ovarian cancer.
There are several types of ovarian cancers; epithelial tumours (being the most common), stromal tumours and germ cell tumours.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
During the initial stages, ovarian cancer may present with no symptoms at all. As the disease progresses, symptoms will start to manifest depending on the extent of the disease. Symptoms may include the following:
· Bloating
· Stomach increasing in size also known as abdominal distension
· Abdominal discomfort
· Constipation
· Bleeding from the vagina
· Indigestion and acid reflux
· Difficulty in breathing
· Fatigue and weakness
· Weight loss
· Feeling full quickly when eating also known as early satiety
· Presence of a mass in the abdomen
· Frequent need to urinate
These symptoms may also be present in other medical conditions. Therefore, if you have the above symptoms it is important to seek medical help in order to confirm what is going on. In cases where ovarian cancer presents without symptoms, the disease may be identified during an ultrasound that was being performed for another reason. This is known as an incidental finding.
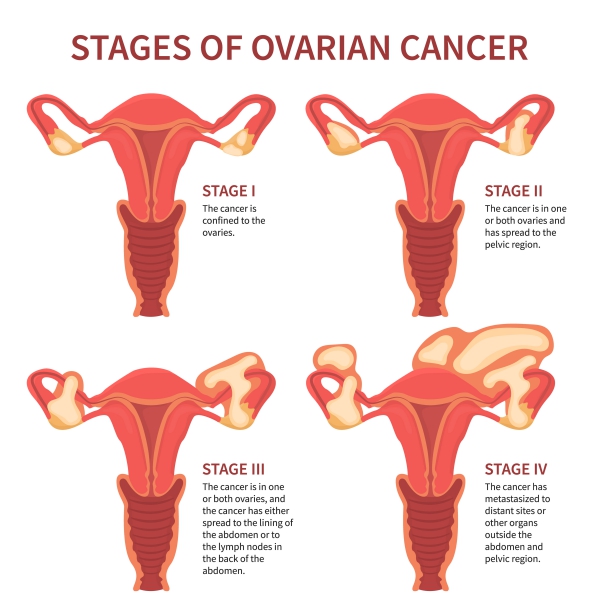
Making a diagnosis
Your doctor will start by asking you a variety of questions about your symptoms and general health. He/she will then proceed by performing a physical examination to look for signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer or to rule out other possible diseases. When the diagnosis of ovarian cancer is suspected, other tests may be requested to confirm the diagnosis. These include:
· Blood Read more