What is fungal nail infection?
Fungal nail infection, also known as onychomycosis, is an infection of the toenails or fingernails caused by a fungus. It affects the nail as well as its surrounding structures including the nail bed and plate. Despite being a non-life-threatening condition, it can cause significant discomfort and disfigurement. It can also impact your quality of life as it will impair your activities of daily living.
Fungal nail infection may be more severe in old people and those who have co-existing medical conditions such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and diabetes. Onychomycosis is the most common nail disorder in adults as it accounts for about 50% of all nail diseases. It most commonly affects toenails compared to fingernails. It is also commonly associated with skin fungal infections. It is more prevalent among old people, diabetic patients and those with a weak immune system. It has also been observed to be more common among males compared to females.
Treatment options for fungal nail infections do exist, however, the treatment may last for a long time.
What are the causes and risk factors for fungal nail infection?
Fungal nail infection, as the name suggests, is caused by a fungus. There are different types of fungus that can result in the condition. Dermatophytes are the most common cause of fungal nail infection. Yeasts and non-dermatophytes moulds can also lead to onychomycosis.

The following increases your risk of ending up with fungal nail infections:
- Having close family members with the same condition
- Increasing age
- Poor general health
- Trauma to your nail
- Living in a warm climate
- Participating in fitness activities
- Having a weak immune system
- Using tight footwear
- Having skin fungal infections
- Smoking
What are the symptoms of fungal nail infection?
Fungal nail infections usually presents with typical symptoms including:
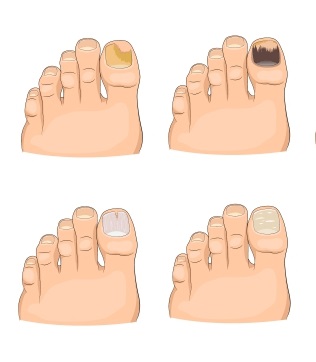
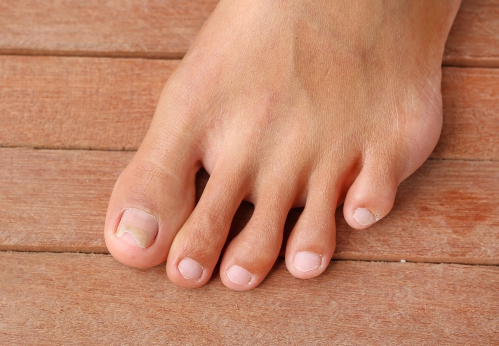
- Nails turning white, brown or yellow
- Appearance of whitish spots on the surface of the nails which eventually spreads if left untreated
- Thickening of nails or change of shape
- Splitting of nails
- Brittle nails
- Shallow or deep holes in the nails
How is the diagnosis of fungal nail infection made?
The diagnosis of fungal nail infection is mostly made with the help of a history and physical examination. Confirmatory tests for fungal nail infections are not usually requested. However, if the diagnosis is doubtful, further tests can be requested.
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation is a tests done to confirm the presence of fungal nail infections. In this procedure, the affected nail is scraped with a special tool in order to obtain a sample for further analysis. This sample is then placed into a special solution containing potassium hydroxide which acts by destroying all cells that are not fungal. The sample is then sent for analysis under a microscope to see if fungus is present.

Other tests may include clipping a sample of the nail and sending it for further analysis.
How is fungal nail infection treated?
The choice of treatment for fungal nail infections depends on the extent and severity of the disease. Treatment options for fungal nail infections include the following:
- Topical antifungals: These medications are directly applied to the affected nails. They work by killing the fungus present. They are used for milder cases of nail fungal infection and in those people who cannot tolerate oral medications. However, it has been observed that topical treatment alone is sometimes not sufficient to treat fungal infections as it may not penetrate the nail adequately. Some examples of topical antifungals include efinaconazole, ciclopirox and amorolfine.
- Oral medications: In some cases, oral therapy may be required as it is more effective in the treatment of onychomycosis. The duration of treatment with oral medications is usually shorter compared to topical therapy. The best treatment for fungal nail infection is the combination of both topical and oral medications. Some examples used include itraconazole and terbinafine.
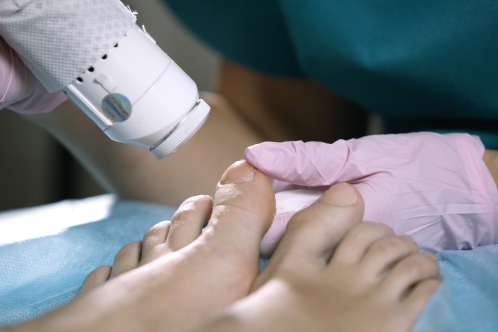
- Laser treatment: There are several laser devices that can help in the treatment of fungal nail infection. Laser therapy is more effective when combined to topical antifungals.
- Surgical care: In some cases, the nail may preferably be surgically removed to allow proper penetration of topical medications.

You should not stop taking/applying your medications even if you cannot see any quick improvement as fungal nail infections may take a long time to cure.
What are the complications of fungal nail infections?
The most common complication of fungal nail infection is disfigurement of nails. This can lead to functional problems as well as psychosocial distress as the nail is not perceived as good looking. Besides the appearance, fungal nail infection can sometimes also be associated with significant pain which can be worsened by anything touching it. It can also serve as a route for frequent skin fungal or bacterial infections.
Prognosis
The main goal of treatment of fungal nail infection is to eradicate the fungus and restore a normal looking nail. It is a condition that takes time and patience to cure. In many people, some nail changes will remain even after treatment and cure. Unfortunately, in many people, the infection can recur. Fungal infections present in fingernails are associated with a better prognosis compared to toenails.
Source:
Shemer, A., 2012. Update: medical treatment of onychomycosis. Dermatologic Therapy, 25(6), pp.582-593.
Goldstein, A., n.d. Onychomycosis: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, And Diagnosis.
Tosti, A., n.d. Onychomycosis Treatment & Management: Medical Care, Surgical Care, Activity.
Goldstein, A., n.d. Onychomycosis: Management.