Atherosclerosis, Fatty deposits, Blocked Arteries, Fatty Plaques, Arteriosclerosis, Heart attack, Stroke
Description : Atherosclerosis, also known as arteriosclerosis, is a common condition which involves the build-up
Article Details :
What is atherosclerosis?
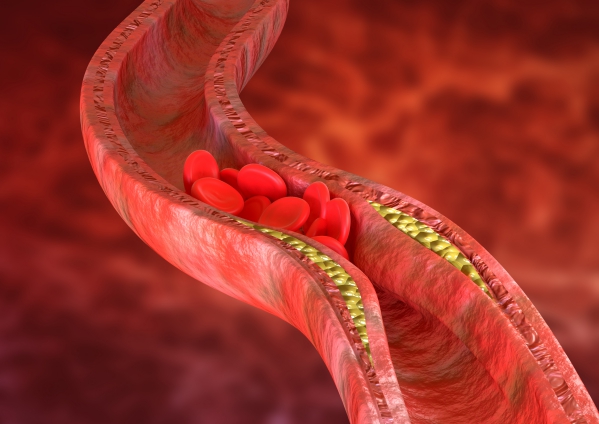
Atherosclerosis, also known as arteriosclerosis, is a common condition which involves the build-up of fatty deposits also known as “plaques” on the inner walls of arteries in the body. This can result in various complications as arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood that contains oxygen from the heart towards other organs and tissues. Atherosclerotic plaques tend to grow bigger with time until the whole lumen of the artery is obstructed, resulting in a blockage in the flow of blood throughout the body. This is the reason why people end up with heart attacks and strokes.
Despite the various advances in the medical field, atherosclerosis remains the main cause of death in both developed and developing countries. In the United States, it accounts for 1 in every 6 deaths, causing the death of more than 400,000 people each year.
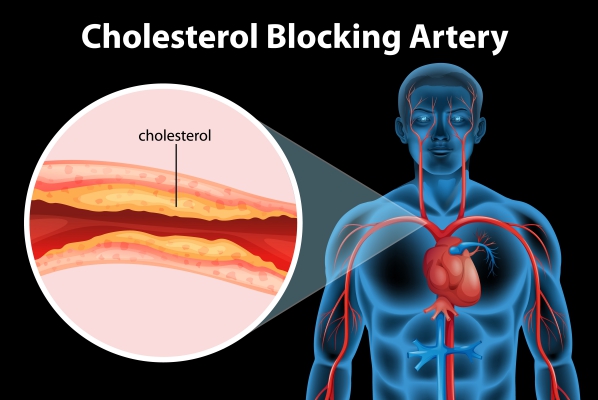
What are the causes and risk factors of atherosclerosis?
The exact cause of atherosclerosis is not known. However, it is a gradually progressive disease that may begin at any age. It may begin when the inner layer of an artery had been injured or damaged. When this happens, inflammatory chemicals and cells are recruited at the site of injury and fat deposits start to form. In some cases, blood clots can even form on the fatty deposits. With time, the fatty plaques may rupture along with the clot, travelling further in the body until it lodges in a smaller artery causing symptoms.
The following factors may increase your risk of having atherosclerosis:
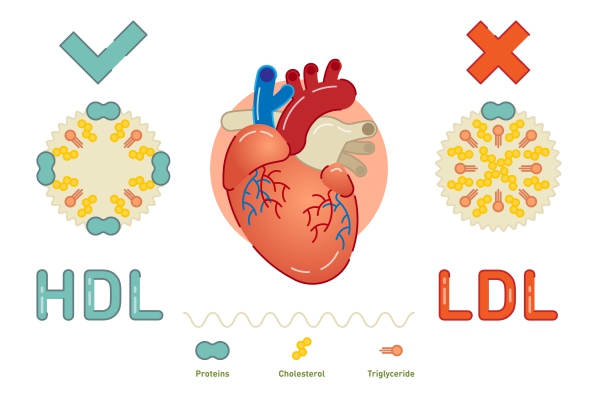
- Having a high cholesterol or triglyceride level in the blood
- Having an elevated blood pressure
- Being diabetic, especially having an uncontrolled blood sugar level
- Being a smoker
- Eating unhealthy foods
- Being overweight
- Not exercising enough
- Having a parent who had the same condition before the age of 50
How is atherosclerosis classified?
Atherosclerosis can affect any artery in the body. The name will depend on the artery affected. These include:
- Carotid artery disease: This is when the disease affects the carotid arteries, which are the arteries responsible for carrying blood from the heart to the brain. If these arteries are affected, stroke may occur.
- Coronary artery disease: This is also known as coronary heart disease. It is when atherosclerotic plaques form in the coronary arteries which are responsible to supply the walls of the heart (muscles) with oxygen rich blood. When coronary artery disease is present, it can result in a heart attack.
- Renal artery stenosis: When fatty deposits form plaques in the renal arteries, which are responsible for supplying the kidneys with blood, high blood pressure or kidney disease may arise.
- Peripheral artery disease: This is a form of atherosclerosis that affects peripheral arteries which are those that supply blood to the arms and legs. This can lead to a variety of symptoms including pain, tingling, or numbness.
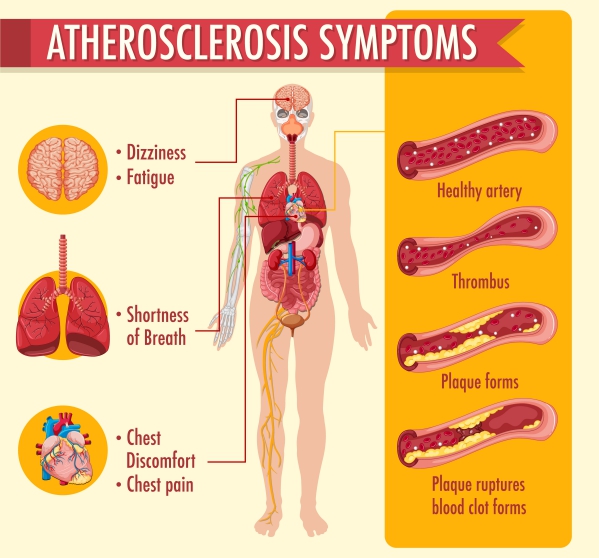
What are the symptoms of atherosclerosis?
The symptoms of atherosclerosis arise due to a decrease in blood flow, especially, blood which is rich in oxygen, to target organs and tissues. The clinical presentation will depend on the location of the obstruction.
In carotid artery disease, the symptoms may include:
- Weakness
- Sudden paralysis or numb sensation in the face or limbs, usually on only one side of the body
- Confusion
- Difficulties in breathing
- Dizziness
- Headache which can be of a sudden onset and severe
- Trouble speaking and understanding
- Visual disturbances
- Loss of balance when walking
In coronary artery disease, the symptoms may include:
- Chest pain
- Discomfort in the chest
- Pain or discomfort spreading to the arms, shoulder or jaw
- Difficulties in breathing
- Chest tightness
- Nausea
- Palpitations
- Rapid heartbeat
- Choking feeling
In renal artery stenosis, the signs and symptoms may include:
- Elevated blood pressure (hypertension)
- Edema (swelling) of the extremities especially at the ankles and feet
- Decreased kidney function
- Changes in urinary frequency
- Presence of protein in the urine
- Drowsiness
- Tiredness
- Weight loss
- Vomiting
In peripheral artery disease, the symptoms may include the following:
- Numbness or weakness in the lower extremities
- Loss of hair on the legs and feet
- Brittle toenails
- Open sores or ulcers on the lower limbs that are difficult to heal
- Legs turning pale or blue
- Shiny skin of the lower extremities
- Difficulty to have an erection in males
- Shrinking of the legs due to wasting of muscles
How is the diagnosis of atherosclerosis made?
To make the diagnosis of Read more