Cerebrovascular accident, Stroke, Thrombus, Paralysis, Blood clot, Brain
Description : Cerebrovascular accident, most commonly known as stroke, is when there is an interruption in blood
Article Details :
What is Cerebrovascular accident?
Cerebrovascular accident, most commonly known as stroke, is when there is an interruption in blood flow through your brain tissue. This can happen as a result of an obstruction or rupture of a blood vessel supplying your brain. When this occurs, your brain no longer receives blood carrying oxygen and important nutrients for it to function properly. Deprivation from these important substances will eventually lead to damage and death of your brain tissue.
If not managed quick, permanent and more severe damage can occur leading to severe impairment and even death. It is therefore very important to seek immediate medical help if you suspect that you or someone is having a stroke.
Cerebrovascular accident is the 5th most common cause of death and a leading cause of major disability in the United States. Transient ischemic attack is a brief episode of neurological dysfunction which looks a lot like stroke but generally lasts for less than 24 hours and does not cause any irreversible tissue damage.
Types of Cerebrovascular accident
There are two types of stroke namely ischemic stroke and haemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke is the most common type and results from the obstruction of a blood vessel with a blood clot. This obstruction prevents the normal flow of blood through the brain hence compromising blood supply and delivery of oxygen and nutrients. There are two mechanisms by which ischemic stroke can happen. The first way is by an embolus. This occurs when a blood clot is formed at a remote body site, for example in the heart, travels all the way to the brain until it gets stuck in an artery. The second way it can happen is by the formation of the blood clot at the site of obstruction in the brain itself.
Haemorrhagic stroke
Haemorrhagic stroke arises when a blood vessel supplying the brain ruptures and leads to leakage of blood, hence not reaching the areas that needs to be supplied. This can happen when the pressure of blood in the artery is too high such as in chronic hypertension.
Risk factors of Cerebrovascular accident
There are several factors that can make you more at risk of having a stroke one day and these are:
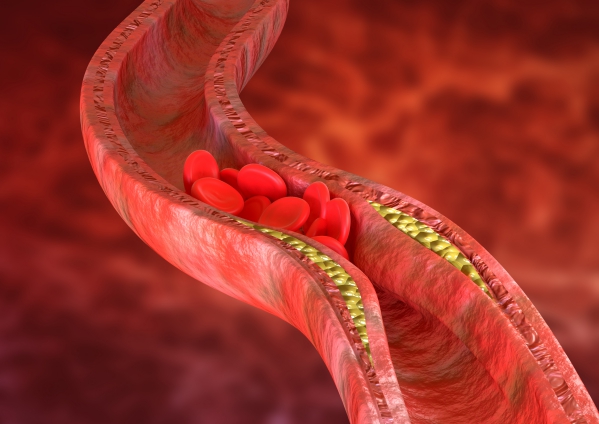
- Atherosclerosis: This is when there is a gradual build-up of fat deposits on the walls of blood vessels. This will slowly obstruct the lumen and also favour the clotting of blood on the plaques.
- Family history: If you have a close family who had stroke, you are also at risk of having it.
- Hypertension: This is one of the most common risk factor for stroke.
- Age: You are at increased risk of having a stroke the older you get.
- Smoking: This increases your risk of having a stroke as the chemical and toxins found in cigarette smoke slowly irritates and damages your blood vessel walls. It also makes your blood more prone to form clots.
- Dyslipidaemia
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Genetic
- Atrial fibrillation
Signs and symptoms
Stroke can present with different symptoms depending on the site of oxygen deprivation in the brain and the duration of the occlusion. Hence, the earlier you seek help, the better the outlook. The symptoms may include:
- Difficulty to walk and move lower limbs
- Paralysis of arm, leg or face on only one side of the body
- Inability to speak and articulate properly
- Vertigo
- Vomiting
- Dizziness
- Loss of coordination
- Loss of sensation
- Visual loss or blurred vision
It is very important to know the symptoms of a stroke for quick recognition and prompt management. As soon as it is suspected, call the emergency services immediately or get to the nearby hospital as soon as possible to decrease the likelihood of severe damage.
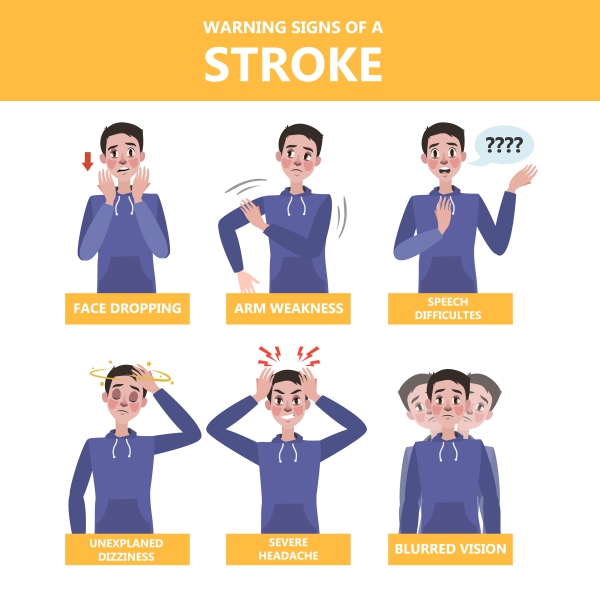

Making a diagnosis
Most of the time the diagnosis of stroke is made clinically by a good clinical history and physical examination. The examination comprises of checking the strength and senses in your limbs, visual examination and assessment of your speech. Your blood pressure will also be measured as this can be the cause of your stroke. Paramedics and members of the public are encouraged to make the diagnosis of stroke on a simple history and examination using the simple mnemonic FAST:
- Face: sudden weakness in the face
- Arm: sudden weakness in one or both arms
- Speech: difficulty speaking or slurred speech
- Time: the sooner treatment can be started, the better
Some other tests can be ordered to look for the cause and the exact location of the stroke including:
- Blood tests: These are done to look for any source of infection, blood sugar levels and your clotting time.
- Angiogram: This is a technique used to visualize your blood Read more