Liver cirrhosis, Liver disorder, Hepatitis, Alcoholic liver disease, Scarring of liver
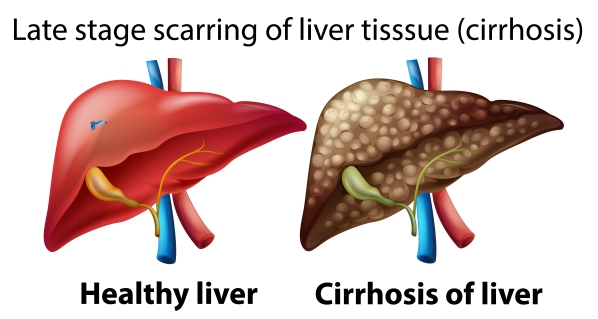
Description : Cirrhosis of the liver is the severe scarring of the liver due to diseases such as hepatitis and
Article Details :
What is liver cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis of the liver is the severe scarring of the liver due to diseases such as hepatitis and alcoholic liver disease. When there is injury to the liver, it will try to repair itself, thus forming scar tissue. The liver is located in the upper right side of your abdomen beneath the ribs. It is responsible for the production of bile which is necessary for the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K. In addition, it also produces clotting proteins and glucose. Furthermore, the liver helps in removing toxic substances from your blood.
Liver cirrhosis is the ninth leading cause of death in the United States. As scarring of the liver progresses, the liver’s ability to perform its functions decrease and becomes a life-threatening condition. The damage done to the liver is often irreversible. However, early diagnosis can stop or slow down the progression of the disease.
What are the causes of liver cirrhosis?
There are several factors and diseases which can result in liver cirrhosis, such as:
- Chronic viral infection of the liver- hepatitis B, C and D.
- Non-alcoholic liver disease- fat accumulation in the liver.
- Alcoholic liver disease.
- Hemochromatosis- iron accumulation in the body.
- Cystic fibrosis- a hereditary disease affecting the lungs and digestive system.
- Wilson’s disease- copper accumulation in the liver.
- Biliary atresia- in this condition the bile ducts are scarred and blocked.
- Hereditary sugar metabolism disorders.
- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency- a hereditary disease that affects the lungs and liver.
- Autoimmune hepatitis- this is when your own immune system attacks your liver cells.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis- this is when scarring of the bile ducts develops.
- Syphilis.
- Drugs- methotrexate, isoniazid, acetaminophen and antidepressants.
- Being overweight or obese.
What are the signs and symptoms of liver cirrhosis?
The signs and symptoms of liver cirrhosis may not be apparent during early stages of the disease. However, as the disease progresses, the following signs and symptoms may arise:
- Feeling very sick, tired and weak.
- Loss of appetite.
- Jaundice- yellowing of the skin and white part of the eyes.
- Unintentional loss of weight.
- Loss of sexual desire (libido).
- Darkening of urine.
- Pale stools.
- Easy bruising and bleeding.
- Peripheral oedema- swelling of the legs.
- Ascites- abdominal distention due to fluid accumulation.
- Nose bleed.
- Gynaecomastia- when males develop breast tissue.
- Irregular menstrual period not related to menopause.
- Confusion and drowsiness.
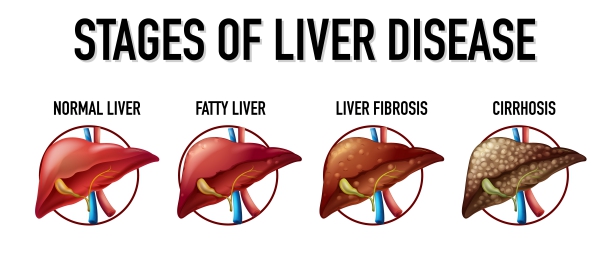
Making a diagnosis
To make a diagnosis, your doctor will first take a detailed history from your to know more about your symptoms. After the history taking, he/she will carry out a thorough physical examination to look for signs of liver cirrhosis, such as:
- Hand tremors
- Jaundice
- Reddened palms and face
- Enlargement of the liver or spleen
- Gynaecomastia
- Confusion
Several tests can be done to confirm the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis, such as:
- Blood tests: complete blood count, coagulation blood tests, serum albumin, liver functions tests and alpha fetoprotein.
- Ultrasound scan of the liver: this is to identify any mass or abnormality within the liver.
- Endoscopy: This is to look for oesophageal varices which occur as a result of portal hypertension due to scarring of the liver.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scan: this is to acquire more detailed information about the structure of the liver.
- Liver biopsy: In this procedure, your doctor take a small piece of your liver, using a needle to send to the laboratory for analysis.
What are the treatments for liver cirrhosis?
The treatment of cirrhosis depends on the underlying causes and the severity of liver damage. The goals of the management are to slow down progression, improve symptoms and prevent complications from the disease. The management of liver cirrhosis include:
- Drugs to manage hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis.
- Weight loss.
- Eating a balanced diet.
- Reducing salt intake.
- Alcohol avoidance: stopping the use of alcohol can significantly improve your health. However, if you are addicted to alcohol, your doctor will recommend you enrolling for a treatment program for alcohol addiction.
- Smoking cessation.
- Doing regular physical Read more