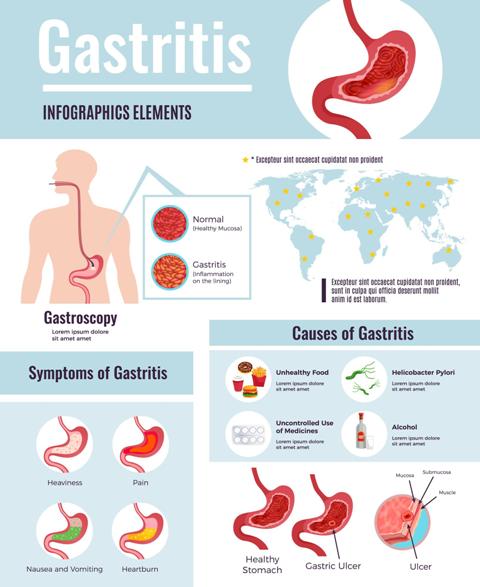
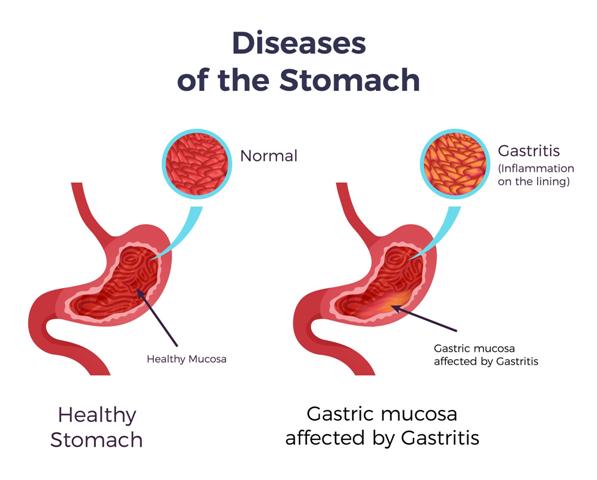
Gastritis is defined as the condition, which involves inflammation of the stomach lining. It is mainly of two types, which include acute gastritis and chronic gastritis. If the acute gastritis in not treated properly then it turns into chronic gastritis and in chronic gastritis, recurrent inflammation of the stomach lining results in changing the activity of gastric mucosal cells
Causes
- H. pylori is a bacteria, which is considered as one of the most common causes of gastritis. It is responsible for causing infection and inflammation of stomach lining and damage the mucous membrane of the stomach in an adverse manner
- Too much consumption of alcohol
- Excessive Smoking
- Prolong consumption of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Swallowing a corrosive substance
- Too much consumption of fatty food
- Excessive consumption of spicy foods
- Radioactive treatments to the lower part of the chest or to the upper abdomen
Signs and symptoms
- Abdominal pain
- Anorexia
- Belching
- Chronic fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Black coloured stool
Nutritional management

Nutrition plays vital role in preventing chronic gastritis. Apart from medicinal therapy, proper nutritional support is also very important for promoting early recovery.
It is better to consume a diet which contains plenty of proteins and less fat. It has seen that various nutritional deficiencies have occurred during this condition like deficiency of Vitamins especially Vitamin B12 and iron and these should be countered by proper nutritional support in order to reduce the severity of the disease
Below points will provide a guideline of the dietary pattern, which should be followed by the patients of chronic gastritis in order to improving their symptoms –
Energy
- Energy should be consumed as per normal RDA
- It should be kept in mind that fat intake should be restricted in this condition thus fat would not be utilized as the energy source so most of the energy requirement should be fulfilled by carbohydrates otherwise body will utilize protein for energy purpose, which is not desired because in this condition body requires protein for anabolic purposes like healing, repairing, tissue re-synthesis, new cell formation etc
Carbohydrates
- 65 to 70% of daily energy should come from carbohydrates
- It is better to consume carbohydrates properly in order to spare the protein
- Consumption of complex carbohydrate is not considered as safe during this condition. As complex carbohydrate contains fibre and consumption of fibre may worsen the condition
- Especially consuming a crud fibre rich diet or consuming too much insoluble fibre can cause further damage to the gastric mucosa and enhances the severity of the disease
- Whereas soluble fibres are well tolerated by the patients thus they can be included in the diet in a soft cooked form. Food like rice, sago, white flour or refined flour can be included in the diet but the consumption of whole wheat, raw food seed and dark green leafy vegetables should be restricted as they contain crud fibre

Protein
- Protein should be consumed adequately as it helps to heal the gastric mucosal damage
- It is better to consume 1 g of protein per kg of ideal body weight
- Consumption of animal protein is very important during this condition as animal protein is considered as high biological value protein as they contain all essential amino acids thus their consumption is thought to be very important for promoting the healing process but the fact is that foods obtained from animal sources contain fat as well thus it is better to select those animal foods, which contain relatively lesser amount of fat than others like skim milk, steamed fish, egg white, chicken and minced meat
- Plant proteins should also be included in the diet such as pulses, legumes, lentils etc

Fat
- Fat consumption should also be restricted in this condition as excessive fat may worsen the inflammation of the stomach lining, which ultimately causes various other complications
- 25 to 30g of fat per day can be consumed
- It is better to focus on the consumption of unsaturated fat like MUFA and PUFA (such as using olive oil, soybean oil, peanut oil as cooking oil, fishes, nut butter etc) as they offer various health benefits but consumption of saturated fat and Trans fat (like red meat, fried foods, margarines, non-dairy coffee creamers) should be strictly avoided as they may worsen the condition
Vitamins
- All vitamins should be consumed as per the RDA but special consideration should be provided on Vitamin A, Vitamin C and Vitamin B12
- It has seen that consumption of a combination of Vitamin A rich food (especially found in green and orange coloured fruits and vegetables) is very helpful for healing the ulcers
- Diet should contain desirable amount of Vitamin C as it helps in accelerating the healing process, whereas it helps in preventing H.pylori infection too thus it helps to decrease the susceptibility of chronic gastritis. It also acts as antioxidant thus its consumption is extremely beneficial
- Consumption of vitamin B12 is very important as there is a deficiency of B12 occurred in this condition thus it is better to consume vitamin B12 rich food or supplements for preventing B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 helps in treating H. pylori infection and also reduces the risk of developing pernicious anemia

Minerals
- All minerals should be consumed as per recommendation but special focus should be given on iron and potassium
- As iron deficiency is very common in this condition thus it is better to consume iron rich food properly in order to decreases the prevalence of iron deficiency
- Whereas potassium is also considered as important mineral, which is essentially required in this condition as potassium along with protein helps in cell and tissue synthesis
Foods that should be included in the diet
Below listed foods should be included in the diet of a chronic gastritis patient as they play vital role in improving the symptoms of gastritis by providing all the nutrients to the body, which are essentially required for this condition –
- Milk especially skim milk
- Yogurt
- Low fat cheeses
- Soybean
- Lentils
- Chickpeas
- Pulses
- Some fruits, which mainly contain soluble fibre like melons, apple, banana etc
- Vegetables that contain soluble fibre but does not contain higher amount of crud fibre like carrot, spinach, zucchini etc
- Vegetable oils
- Egg white
- Fish
- Lean meat
- Natural juices
Foods that should be excluded from the diet
There are various foods, which are responsible for making the gastritis worsen and also accountable for irritating the stomach thus it is better to avoid those foods for ensuring healthy recovery and these foods include –

- Acidic foods, such as tomatoes
- Spicy foods
- Fried foods
- Sodas and sweetened drinks
- Alcohol
- Carbonated beverages
- Tea
- Coffee
- Pickled foods
- Spicy peppers
- Mustard grains
- Chocolate
- Processed meat
General dietary consideration
- It is better to consume small amount of food in frequent intervals
- Heavy breakfast should be consumed and breakfast should not be skipped
- Staying in empty stomach for long period of time is not safe as it may worsen the condition
- Foods, which exert anti-inflammatory activity (like spinach, olive oil, fish, carrot, apple etc) should be included in the diet as they help to treat the inflammation of stomach lining hence promotes recovery
- It is better to consume probiotic foods as probiotics help in treating stomach complications especially those complications, which are caused by Helicobacter pylori thus diet should contains some probiotics like yogurt, kombucha, sauerkraut, kimchi etc

Source:
Li, Y., Su, Z., Li, P., Li, Y., Johnson, N., Zhang, Q., Du, S., Zhao, H., Li, K., Zhang, C. and Ding, X., 2020. Association of Symptoms with Eating Habits and Food Preferences in Chronic Gastritis Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2020.
Rugge, M. and Genta, R.M., 2005. Staging and grading of chronic gastritis. Human pathology, 36(3), pp.228-233.
Sandi, Y.D.L., Fitriani, A., Lismayanti, L., Srinayanti, Y. and Widianti, W., 2021. Prevalence and Correlation of Knowledge Level, Stress, Diet Compliance and Quality of Life in Gastritis Patients. Genius Journal, 2(1), pp.22-29.
Sipponen, P. and Maaroos, H.I., 2015. Chronic gastritis. Scandinavian journal of gastroenterology, 50(6), pp.657-667.
Varbanova, M., Frauenschläger, K. and Malfertheiner, P., 2014. Chronic gastritis–An update. Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology, 28(6), pp.1031-1042.