Ectopic pregnancy, Emergency, Miscarriage
Description : Ectopic pregnancy is the result of a problem in the conception process. In a normal pregnancy, the
Article Details :
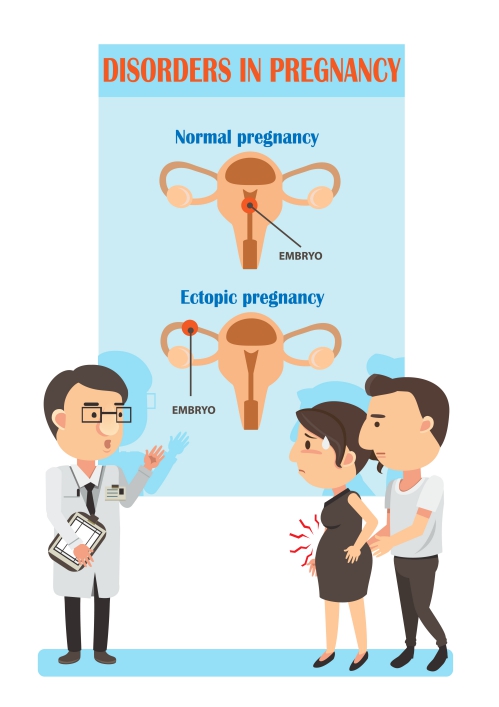
What is ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy is the result of a problem in the conception process. In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus where the embryo will develop into a foetus. In ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants anywhere outside of the uterus.
The most common site where this occurs is in the fallopian tubes which are tubes through which released egg travels from the ovaries to reach your uterus. This is also known as tubal pregnancy. Other sites may include the ovaries, the cervix or the abdominal cavity. Ectopic pregnancy inevitably leads to the death of the foetus. If not diagnosed and treated in time, it can become life-threatening for the mother.
With time, more and more cases of ectopic pregnancy are being reported. This may be due to the increased ability to make the diagnosis early.
Causes and risk factors of ectopic pregnancy
Several factors have been identified as increasing the risk of or causing ectopic pregnancy. These include:
- Damage to fallopian tubes: Inflammation and infection of the fallopian tubes can cause damage to the tubes, increasing the risk of implantation in their wall. These include pelvic inflammatory disease and salpingitis. Abdominal or other gynaecological surgeries may also make you more at risk in the future.
- History of previous ectopic pregnancy: If you already had at least one episode of ectopic pregnancy in the past, you are 7-13 times more at risk of having it again.
- Smoking: Smoking affects the way the fallopian tubes work in guiding the released egg towards the uterus. It causes damage to the cells whose function is to sweep the egg along the tube. Therefore, it increases the risk of a tubal pregnancy.
- Hormonal contraception: This affects the fallopian tubes in the same way as smoking. Taking progesterone-only contraception and progesterone intrauterine devices (IUDs) can increase your risk of having an ectopic pregnancy.
- Long period of infertility: Women who have not been able to conceive for a long period of time are more at risk of having an ectopic pregnancy. Assisted methods of reproduction such as in vitro fertilisation can also double your risk.
- History of multiple sexual partners: If you have or had several sexual partners, you are more prone to end up having an ectopic pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms that occur in ectopic pregnancy depends on the severity, that is, whether the ectopic pregnancy is ruptured or unruptured. A ruptured pregnancy can be life-threatening as it can cause severe bleeding inside the abdomen.
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy include the following:
- Vaginal bleeding: One of the classic symptoms of ectopic pregnancy include vaginal bleed. The volume of blood as well as the pattern of bleeding vary among women. In some women, it can present as a scant brown staining, while in others, it can arise as a haemorrhage. It is usually preceded by a period without menstruation, therefore, some people may think that the bleeding from the ectopic pregnancy is their actual menstruation.
- Pain in the abdomen: Even if the timing, character and severity of the abdominal pain may be different in different women, it is a common symptom found in ectopic pregnancy. The pain becomes more and more perceptible as the tubes become increasingly distended. This can eventually lead to rupture which presents with a more severe and abrupt pain.
Other non-specific symptoms of ectopic pregnancy include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fullness in the breast
- Fatigue
- Cramping
- Recent painful sexual intercourse
- Shoulder pain
If rupture has occurred, the following signs and symptoms may be present:
- Severe pain
- Light-headedness
- Dizziness
- Decreased blood pressure
- Fainting
- Shock
Making a diagnosis
To make the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will start with taking a good history from you. This will involve questions about your symptoms and your gynaecological history. He/she will then proceed with a physical examination. The main goal of the evaluation for ectopic pregnancy is to confirm if you are pregnant and evaluate whether your life is threatened. It is very important to make the diagnosis the earlier possible to minimise the risk of rupture and death. The tests that can be done include:
- Beta-Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (B-HCG) levels: B-HCG is a substance that is released by the developing placenta, hence is present only during pregnancy. It can be detected in the woman’s urine or blood. However, blood serum HCG is the preferred test to confirm pregnancy. If you present with the symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, it is of utmost importance to check for the levels of B-HCG.
- Ultrasound scan: In this test, sound waves emitted by a transducer are used to visualise the reproductive organs and abdomen. The most commonly used ultrasound in suspected cases of ectopic pregnancy is the transvaginal ultrasound. In this procedure, the probe is inserted through your vagina which enables better visualisation of the inside of the uterus. If no pregnancy Read more