Calcium , vitamin, Ca
Description : Calcium is one of the most important minerals of human body which acts as the main constituents of
Article Details :
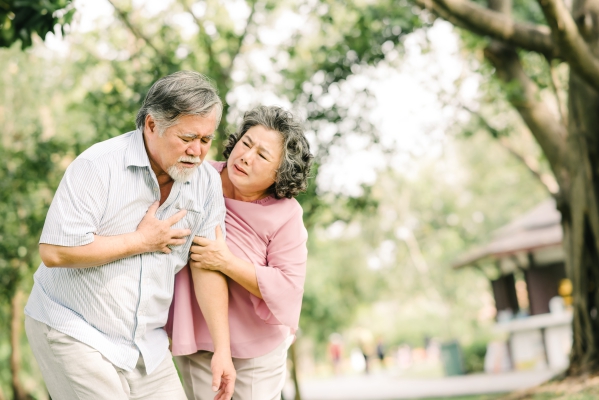
Calcium is one of the most important minerals of human body which acts as the main constituents of bones and teeth. Calcium also helps in muscle contraction, transduction of nerve impulses, hormone secretion and performs many other important functions of body. Several researches have shown that adequate intake of calcium is very much important especially in early adulthood to obtain maximum level of bone mass that helps to prevent osteoporosis in later age (Marcinow et al., 2017). Calcium deficiencies are also very common especially among middle aged person (females are more prone) and causes various complications such as bone and joint disorders, hypertension, cardiac problems, impaired muscle contraction and abnormalities in nervous stimulus transduction. Several epidemiological studies have suggested that fortification of foods and water with calcium is an important remedial action to overcome calcium deficiency and helps to promote bone health (Cormick and Belizán, 2019).
Five important facts regarding calcium
- Among all minerals, calcium is considered as the most abundant trace element of human body
- About 1 to 1.5 kg of calcium is present in an adult body among which 99% of calcium is found in bones and teeth
- About 1% of calcium is found outside the skeletal muscle and plays several important biochemical roles
- The normal range of serum calcium is 9 to 11 mg per dl among which about 5mg of calcium per dl is present in ionized form, which is considered as the functionally active form of calcium in human body
- It is essential to consume Vitamin D along with calcium as it helps to increase calcium absorption
Sources
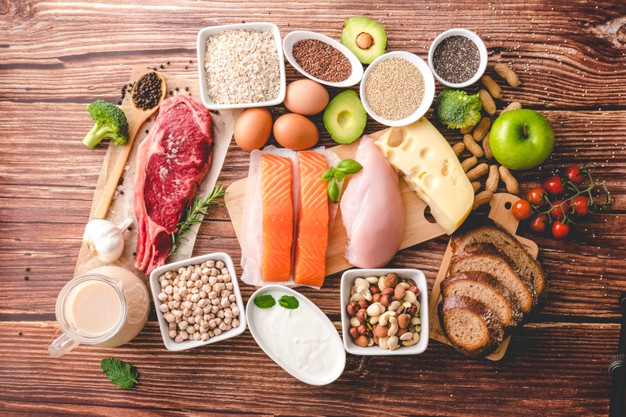
Foods rich in calcium are listed below –
- Milk
- Soybean
- Yogurt
- Cheese
- Tofu
- Sesame seeds
- Almond
- Fishes such as sardines, salmons (one can eat the bones of this kind of fish)

- Coriander leaves
- Broccoli
- Cabbages
- Egg yolk
- Beans
- Nuts
Recommended Dietary allowance
- Adult men and women should consume 600 to 800 mg of calcium per day to fulfill its requirements
- Pregnant women, lactating women and women of post-menopausal phase have an increased demand for calcium. It is better to consume 1200mg of calcium daily to meet the increased requirement
- Boys and girls between the age group of 1 to 18 years should consume 0.8 to 1.2g of calcium daily
- Whereas it is beneficial for infants (0 to 12 months of age) to consume 300 to 500 mg of calcium per day
Factors affecting calcium absorption
Proper absorption of calcium is very much important as calcium is only able to serves its function when it gets absorbed completely. Generally, calcium is absorbed in duodenum and requires two hours for completing the absorption process.
The below table will show an overview of factors interfering with calcium absorption –
|
Factors increases calcium absorption |
Factors decreases calcium absorption |
|
|
One should consider all the above stated factors for maximizing their calcium absorption and utilization.
Health benefits
Role on bone and teeth formation
- Calcium is the principal constituents of bone and teeth. It binds with phosphorus and forms calcium phosphate, which is responsible for mineralizes bone and teeth, that enhances their strength
- During school going age, in adolescence period and in early adulthood calcium is exclusively required for contributing the development of bones. After completion of respective growth phases, when an individual stops growing then calcium is required for maintaining the bones
- It also helps to slow down the losses of bone mineral density and helps to reduces the risk of developing bone deformities